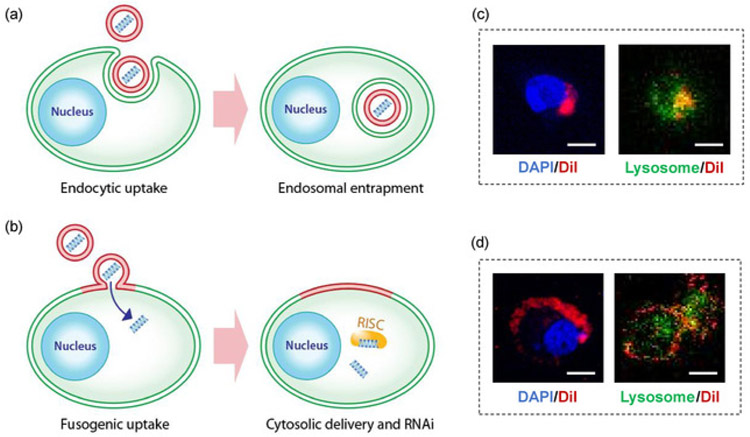
Figure 1: Fusogenic porous silicon nanoparticle system (F-pSiNP).
(a) Schematic showing endocytic uptake of conventional nanoparticles and subsequent endosomal entrapment, (b) Schematic showing fusogenic uptake of the F-pSiNPs and subsequent cytosolic delivery of the siRNA payload, (c) Confocal microscopic image of a CAOV-3 cell that has endocytosed non-fusogenic pSiNPs that were loaded with DiI lipophilic dye. CAOV-3 cells were grown to 80% confluence in a 6 well-plate, and treated with 10 μL of nanoparticles, and incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 for 15 min. The cells were fixed in 1% paraformaldehyde to be mounted on glass slides with DAPI, dried and kept in the dark until examined by confocal microscopy. (D) Confocal microscopic image of a CAOV-3 cell that has taken up fusogenic pSiNPs that were loaded with DiI lipophilic dye. Cells were pre-stained with LysoTracker Green for 1 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2 according to manufacturer’s instructions. The cells were then washed PBS three times, and were treated with 10 μL of Dil-loaded particles for 15 min. The cells were washed with PBS three times to remove any particles that were not taken up, and the wells were filled with 1 mL of PBS and immediately taken for live-cell imaging by confocal microscopy; DAPI represents nuclear stain and Lysosome represents lysosomal staining by LysoTracker Green; scale bar represents 10 μm.