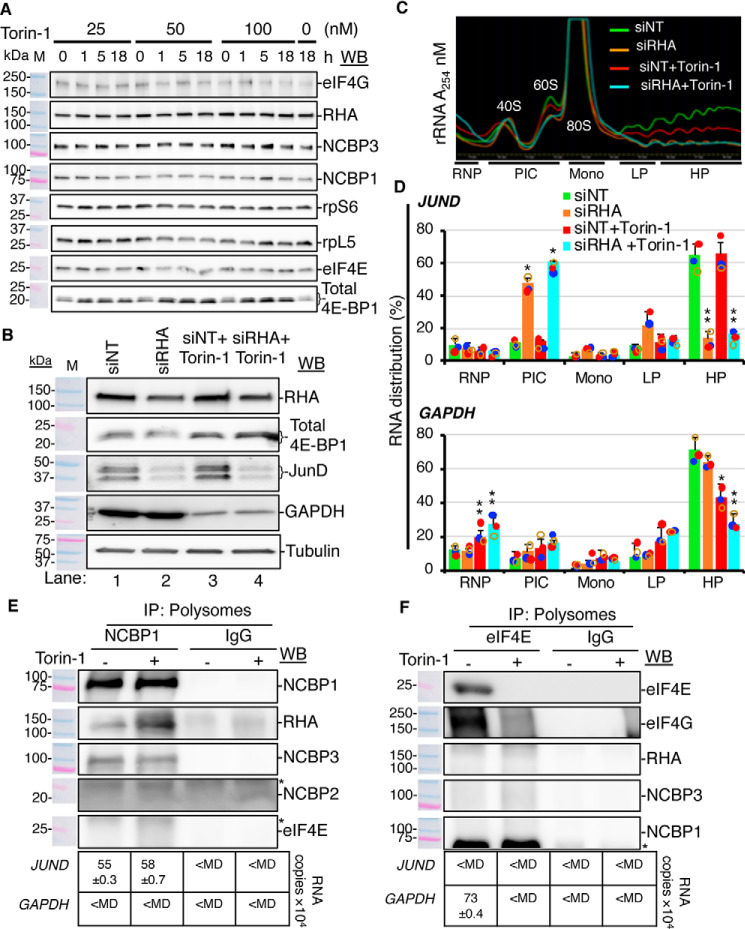
Figure 6.
RHA is essential for mTOR-resistant translation of JUND. A, HEK293 cells were treated with mTOR inhibitor Torin-1 (0–100 nm) for 0–18 h, and the cell lysates were analyzed by WB with the indicated antisera. B, cells transfected with siRNA targeting RHA (siRHA) or nontargeting control (siNT) and treated with 50 nm Torin-1 or 0.2% DMSO for 18 h were analyzed by WB with antiserum to RHA, 4E-BP1, JUND, GAPDH, or tubulin (loading control). C, A254 spectrometry of the sucrose gradient showing rRNA distribution in the fractions. PIC, preinitiation complex composed of 40S and 60S RNPs; Mono, monosome (80S); LP, light polysome (two or three polysomes); HP, heavy polysome (four or more polysomes). D, JUND and GAPDH RNA copies were analyzed by RT-qPCR and calculated relative to standard curves. The graphs present the distribution of the RNA across the gradients. The results represent the means of three independent experiments (bars) with standard deviation. The colored circles indicate the values from the individual experiments. Statistical significance is indicated with asterisks: *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.005. E and F, the light and heavy polysome fractions were combined, and proteins were precipitated and subjected to IP with NCBP1 or eIF4E antiserum. Co-precipitates were subjected to WB with the indicated antiserum or RNA extraction followed by RT-qPCR. Isotype-specific IgG were used as negative controls. The antiserum detected the specific proteins on the immunoblots, as shown relative to the prestained molecular mass markers (M). The same image of the molecular mass markers was used for each panel. *, nonspecific band. The table below each WB panel shows the number of copies of JUND and GAPDH relative to IgG control detected by RT-qPCR.