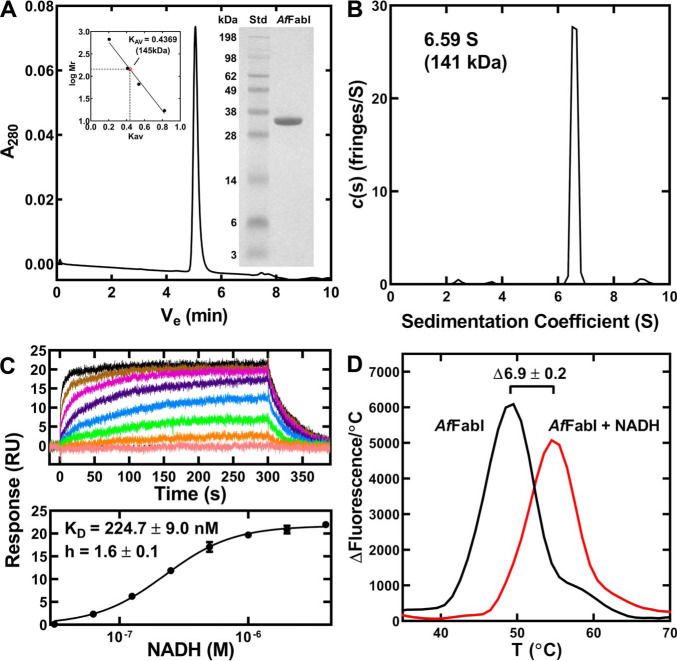
Figure 3.
AfFabI oligomerization and NADH binding. AfFabI was purified by affinity and gel filtration chromatography. A, AfFabI migrated as a single 145 kDa species (Ve = 5.058 min) on a calibrated XBridge BEH SEC 200 Å 3.5-μm column (136 kDa theoretical mass). Insets, gel electrophoresis shows the purity of AfFabI (34 kDa) along with the indicated molecular weight standards (Std). The standard curve for the XBridge BEH SEC column used thyroglobulin (669 kDa), immunoglobin (150 kDa), BSA (66.4 kDa), and myoglobulin (17 kDa). B, the sedimentation velocity profiles (fringe displacement) were fitted to a continuous sedimentation coefficient distribution model c(s). AfFabI sedimented as a 141 kDa tetramer with a sedimentation coefficient of 6.59 S. C, surface plasmon resonance sensorgrams depicting one experiment to determine NADH binding to AfFabI (top panel). The data from three independent titrations were fit to the Hill equation using GraphPad Prism software to calculate the KD and Hill coefficient (h). Mean ± S.E. (n = 3). D, protein thermal denaturation analysis was used to determine the stabilization of AfFabI by NADH. Assays contained 10 μm AfFabI (black) or 10 μm AfFabI + 100 μm NADH (red).