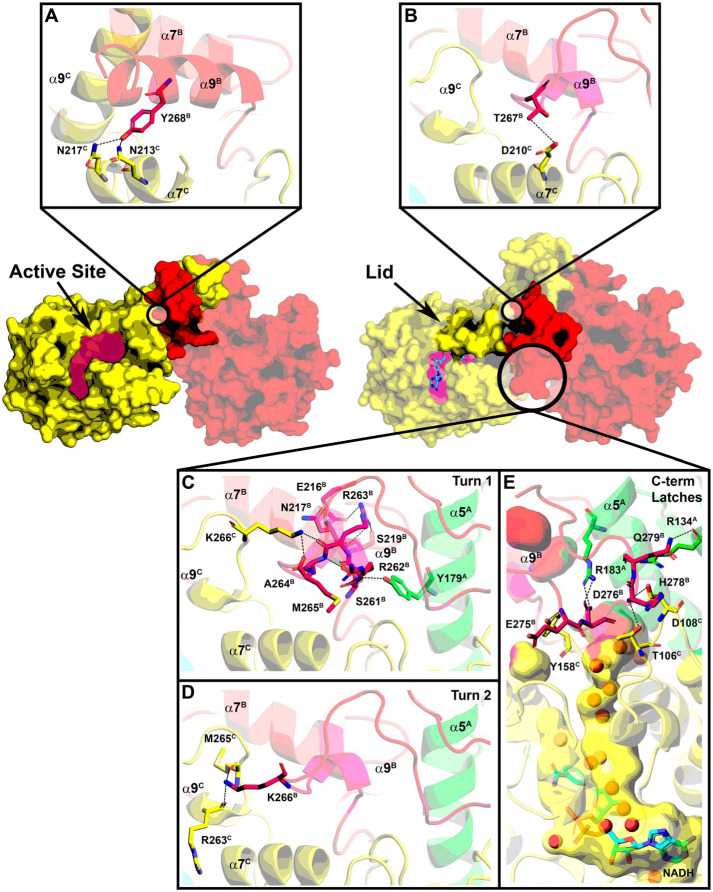
Figure 9.
Creation of the NADH-binding site. The active site lid is disordered in the absence of NADH and helix α9B (red) is coiled around α9C (yellow) along the R axis. NADH (cyan) binding to the active-site crevice orders the lid. A, Tyr-268B in the second turn of helix α9 in the AfFabI structure forms hydrogen bond interactions with Asn-217C and Asn-213C in the second two turns of α7C. B, following NADH binding, the unwound α9B slips along α7C. The Thr-267B side chain on α9B forms a hydrogen bond interaction with Asp-210C in the first turn of α7C. C, residues in the first turn of α9 in the AfFabI structure become an ordered loop in AfFabI·NADH with multiple hydrogen bond interactions with the other protomer. D, Lys-266B from the second turn of α9 in AfFabI form hydrogen bond interactions with Arg-263C and Met-265C from α9C in AfFabI·NADH. E, hydrogen bond interactions between the disordered carboxyl terminus of AfFabI with the other protomers in AfFabI·NADH. The backbone amine of Glu-275B forms a hydrogen bond with the Tyr-158C side chain, the side chain of Asp-276B forms a hydrogen bonds to the side chain of Arg-183A (on α4A), the backbone amine of His-278B forms a hydrogen bond interaction with the Thr-106C and Asp-108C side chains and the backbone carbonyl and side chain from Gln-279B forms hydrogen bonds with the side chain and backbone carbonyl of Arg-134A from α5A.