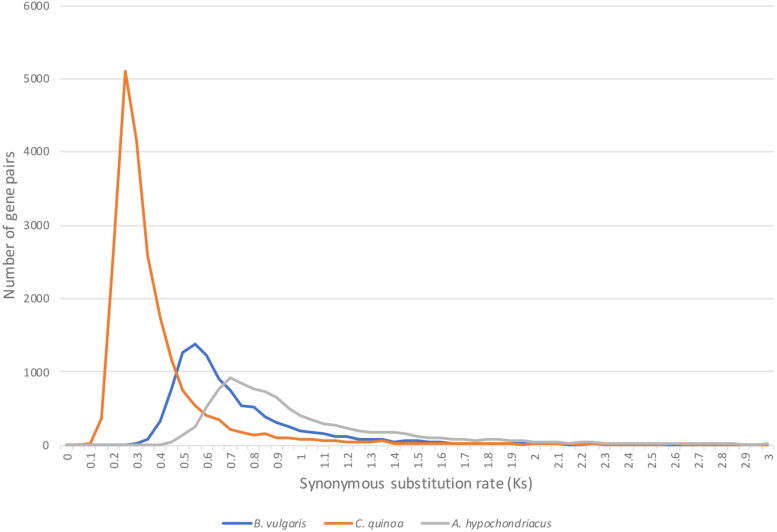
FIGURE 6.
The age of the evolutionary split between A. hortensis and B. vulgaris, C. quinoa, and A. hypochondriacus was estimated using the rate of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site (Ks) calculated from othologous gene pairs. C. quinoa is most closely related to A. hortensis, with a clear peak present at Ks = 0.25, followed by B. vulgaris (Ks peak = 0.55), while A. hypochondriacus is more distantly related, with a Ks peak = 0.7.