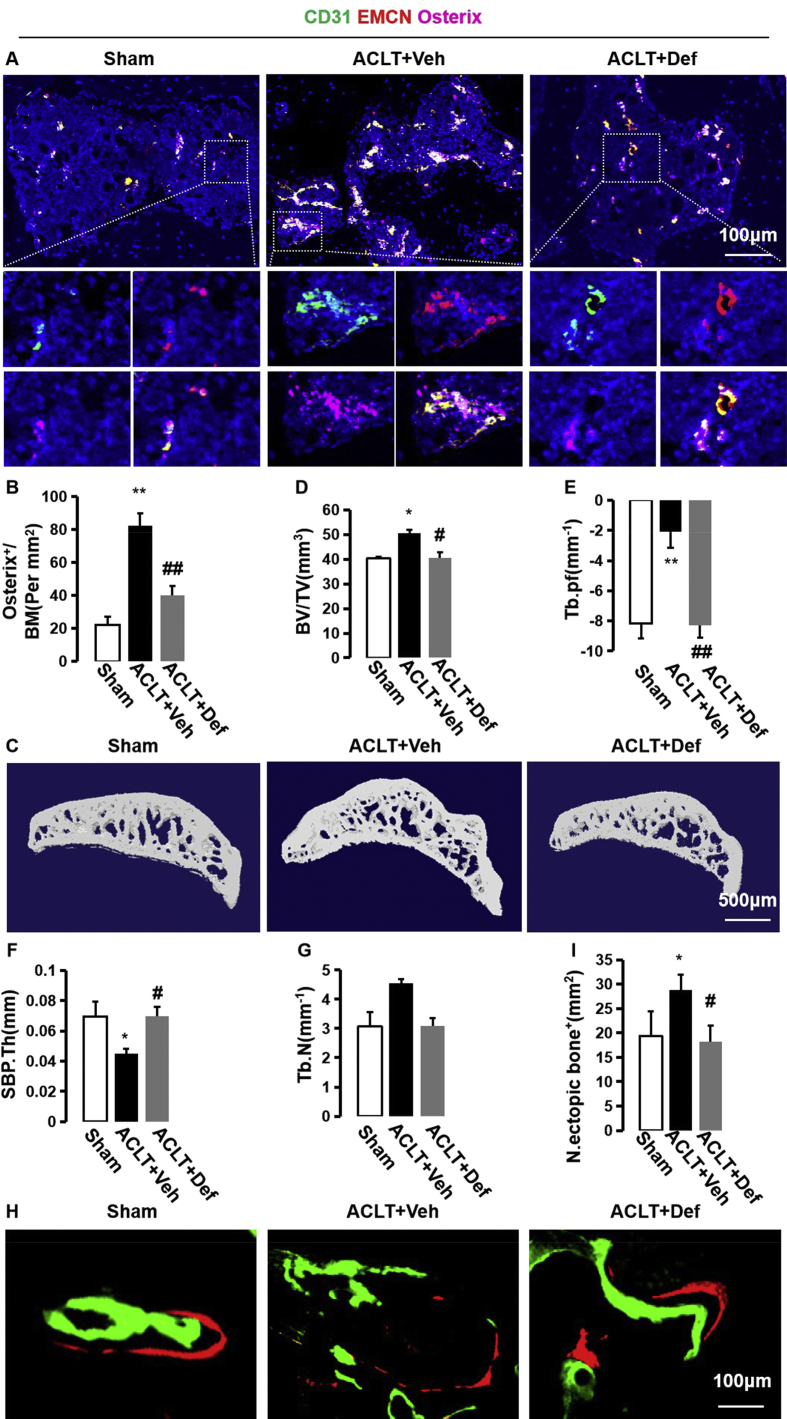
Fig. 2.
Defactinib inhibits h-type vessel-induced abnormal bone formation in subchondral bone. (A and B) Confocal images (A) and quantification of CD31 and endomucin-positive cells (CD31: green; endomucin: red; merge: yellow) and Osterix+ (purple) cells. n = 10 per group. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Representative three-dimensional micro-CT images of the sagittal views of the subchondral bone medial compartment. Scale bar, 500 μm. (D–G) Quantitative micro-CT analysis of the tibial subchondral bone of the bone tissue relative to the total tissue volume (BV/TV). (D) Trabecular pattern factor (Tb.pf). (E) Subchondral bone plate thickness (SBP.Th). (F) Trabecular N (Tb.N) (G). n = 10 per group. (H) Fluorochromes xylenol orange and calcein green staining in the subchondral bone after surgery. Scale bar, 100 μm. (I) Quantification of abnormal bone formation in the subchondral bone. n = 5 per group. Sham = sham controls; ACLT + Veh = vehicle-treated ACLT mice; ACLT + Def = Defactinib-treated ACLT mice. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 compared to sham. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 compared to vehicle.