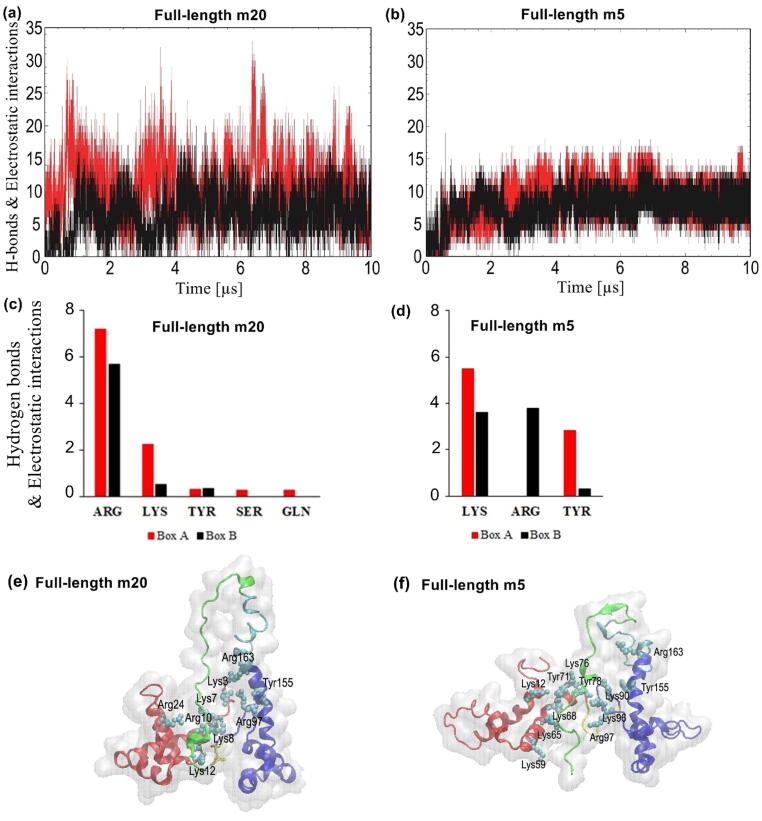
Fig. 6.
Hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions formed between the acidic tail and the boxes. Time evolution of the average number of hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions between the acidic tail and Box A (red) and Box B (black) in (a) full-length m20 and (b) full-length m5. Amino acid residues with the largest number of hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions from each box in (c) full-length m20 and (d) full-length m5. Snapshots show amino acids forming hydrogen bonds or electrostatic interactions in (e) full-length m20 and (f) full-length m5. In each figure (e) and (f), the red regions represent Box A, blue regions represent Box B, yellow portions represent the linker between boxes, cyan regions represent the linker between Box B and the acidic tail, and light green portions represent the acidic tail. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)