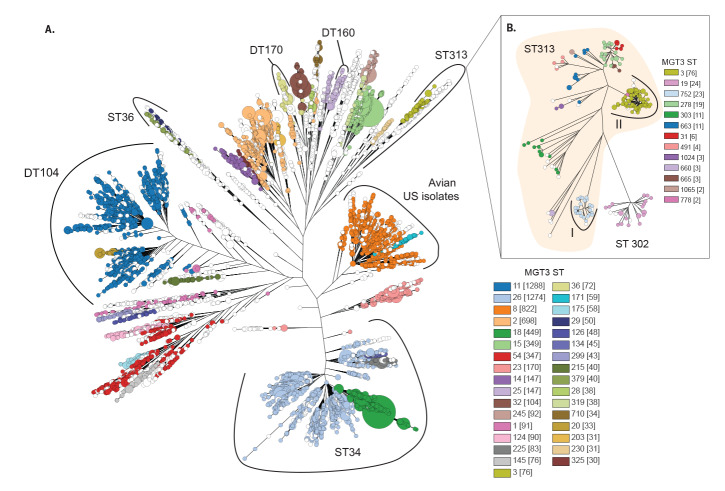
Figure 3.
Salmonella Typhimurium population structure obtained with multilevel genome typing (MGT) level 3 sequence types (n = 9,096 genomes)
MLST: multilocus sequence typing; ST: sequence type; US: United States.
A. A dendrogram of 9,096 isolates derived from the allelic profiles of the largest MGT9 MLST scheme. STs with more than 30 isolates were marked. Branch lengths are log scale for clarity. Phage types and seven-gene MLST STs of interest are marked. One clade of isolates is almost entirely composed of isolates derived from birds in the United States and is identified by MGT3 ST8 and ST171. DT104 is identified by MGT3 ST11, seven-gene MLST ST34 (monophasic Typhimurium) is identified by MGT3 ST26, ST18 and ST225.
B. A subtree derived from section A showing seven-gene MLST ST313 as well as its closest outgroup ST302. Previous studies have identified two lineages of ST313 that cause invasive salmonellosis. These lineages, I and II, are shown and can be defined by MGT3 ST752 and MGT3 ST3 respectively. Importantly MGT3 can distinguish both invasive lineages from other ST313 isolates that do not cause invasive disease.
Numbers in square brackets denote the number of isolates assigned each ST.