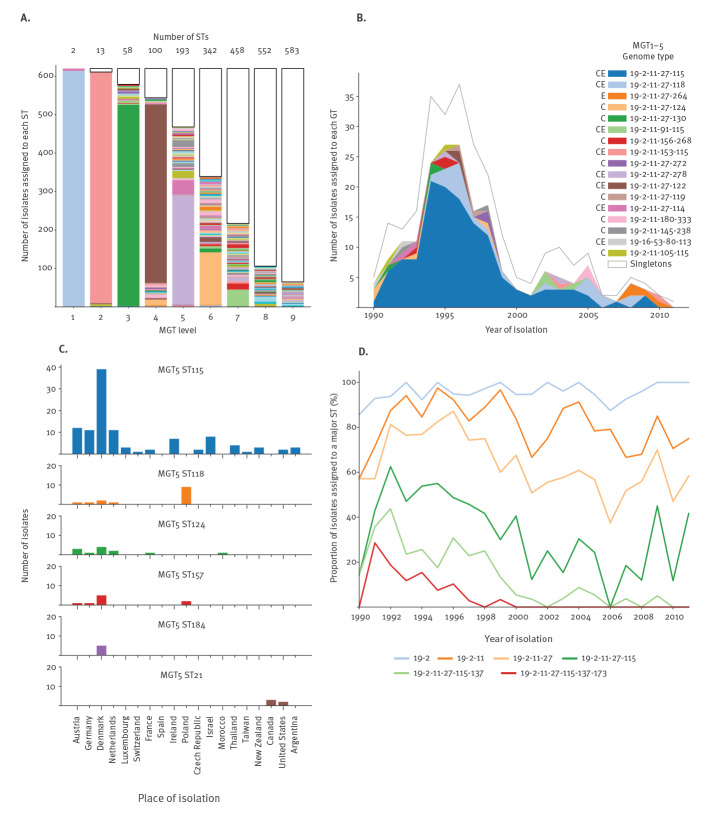
Figure 4.
The multilevel genome typing describes temporal and spatial trends and clusters in Salmonella Typhimurium phage type DT104 (n = 619)
C: clinical source (panel B); E: environmental source (panel B); GT: genome type; MGT: multilevel genome typing; ST: sequence type; UK: United Kingdom.
A. 619 DT104 isolates assigned to STs at each MGT level. STs with two or more isolates are grouped into coloured blocks while STs assigned to only one isolate are grouped into one category shown as the white box with black outline. The number of STs identified for each scheme is shown above each column.
B. Temporal distribution and source type of MGT1–MGT5 GTs in the UK from 1990 to 2011. 273 isolates used in Mather et al. (2013) [13] that were isolated in the UK were classified using GTs. The number of isolates were distributed according to their year of isolation and stratified by partial GTs including MGT levels 1 to 5. C denotes clinical and E denotes environmental sources. If both are present, strains annotated with the GT come from both sources. If only one is shown all strains annotated with the GT come from that source type. GTs occurring in one isolate were grouped together as ‘singletons’ for clarity.
C. Geographical distribution of MGT5 STs. 289 strains used in Leekitcharoenphon et al. (2016) [53] were classified using MGT5. MGT5 STs occurring in more than three isolates are shown. MGT5 ST115 is by far the largest group and is the most common ST in most countries. MGT5 ST118, ST124 and ST157 are generally restricted to north-western Europe and Poland. MGT5 ST184 is restricted to Denmark while MGT5 ST21 is restricted to North America.
D. The proportion of 619 isolates sequenced in Leekitcharoenphon et al. (2016) and Mather et al. (2013) [13,53] assigned to the most common MGT2–7 GTs over time. The major GT for each level was determined and the percentage of isolates in a given year classified into that GT is shown. With the exception of MGT2 and MGT3, all other MGT levels show a reduction in the major type over time.