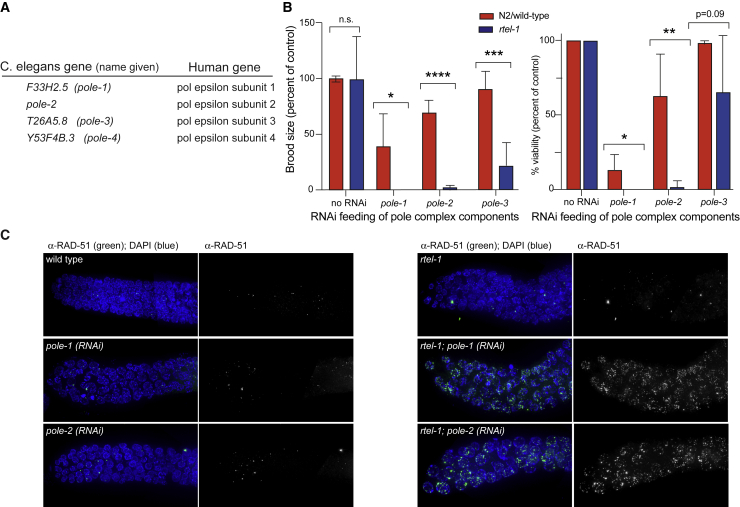
Figure 1.
Knockdown of Polymerase Epsilon Components by RNAi Causes Synthetic Lethality in rtel-1 Mutant Background
(A) C. elegans gene names of the four polymerase epsilon components and their corresponding human homologs.
(B) Total brood size and percent viability after feeding either no RNAi or RNAi for pole-1, pole-2, or pole-3 in the N2(wild-type) or rtel-1 mutant. Brood size and percent viability are both normalized based on untreated N2(wild-type) or rtel-1 control animals. (∗p < 0.05, ∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant).
(C) RAD-51 staining of mitotic zones of N2(wild-type) or rtel-1 animals fed either with no RNAi, pole-1, or pole-2 RNAi.
Images are composites of several images stitched together. Error bars in all graphs represent standard deviation (SD) of the mean.