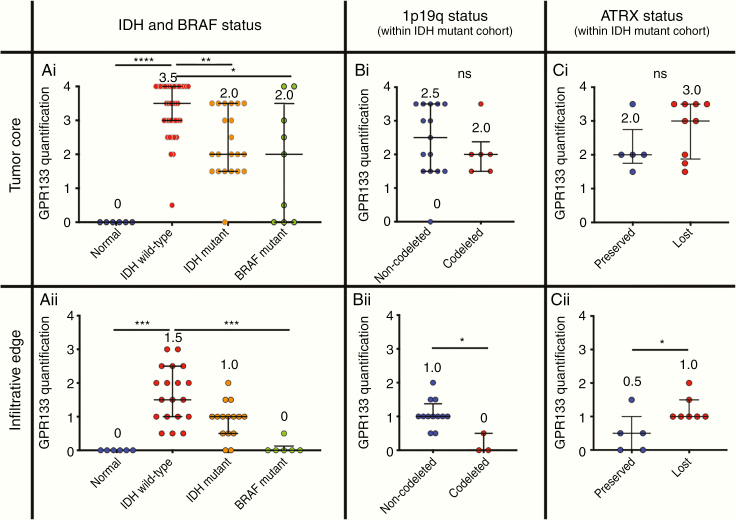
Figure 4.
Influence of IDH and BRAF mutations on GPR133 expression. (Ai) GPR133 expression, as assessed by immunohistochemistry, is higher in the core of IDH wild-type gliomas compared to IDH mutant and BRAF mutant gliomas (P < .0001, Kruskal–Wallis test; post hoc Dunn’s *P < .05; **P < .01; ****P < .0001). (Aii) Similar comparisons in the infiltrative edge of such tumors (P = <.0001, Kruskal–Wallis test; post hoc Dunn’s ***P < .0005). (Bi) There is no difference in GPR133 expression within the core of 1p19q codeleted versus non-codeleted IDH mutant gliomas (Mann–Whitney test; ns, P > .05). (Bii) The infiltrative edge of non-codeleted IDH mutant gliomas shows higher levels of GPR133 expression (Mann–Whitney test; *P < .05). (Ci) GPR133 expression is equivalent within the core of IDH mutant gliomas with preserved or lost ATRX (Mann–Whitney test; ns, P > .05). (Cii) The infiltrative edge of ATRX loss IDH mutant gliomas shows higher levels of GPR133 expression (Mann–Whitney test; *P < .05).