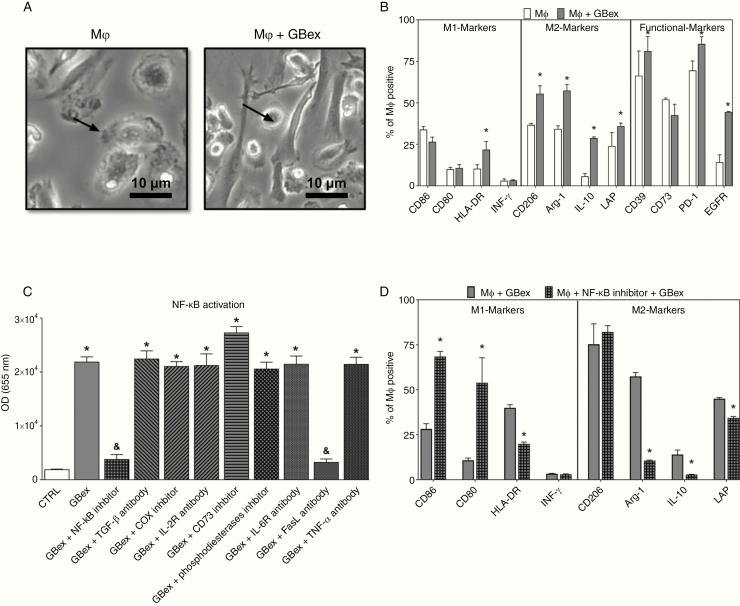
Figure 4.
GBex induced M2-like polarization via NF-κB activation in macrophages. (A) Representative phase-contrast microphotographs of macrophages after treatment with GBex for 72 h. Note alterations of macrophage morphology in Mφ + GBex (bar equals 10 µm). (B) Macrophage polarization after treatment with GBex for 72 h. The panel shows M1 markers (CD86, CD80, HLA-DR, and INF-γ), M2 markers (CD206, Arginase-1, IL-10, and LAP), and functional markers (CD39, CD73, PD-1, and EGFR). (C) Biological activity of GBex (20 µg) on the activity of the NF-κB pathway macrophages. *Significantly different from CTRL and &significantly different from GBex at P<0.05. (D) Macrophage polarization after treatment with the NF-κB inhibitor for 30 min followed by the addition of GBex. Values represent the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. Data were analyzed by ANOVA followed by post hoc comparisons (Tukey–Kramer test). *Significantly different from macrophages+ GBex group at P < 0.05.