Figure 4.
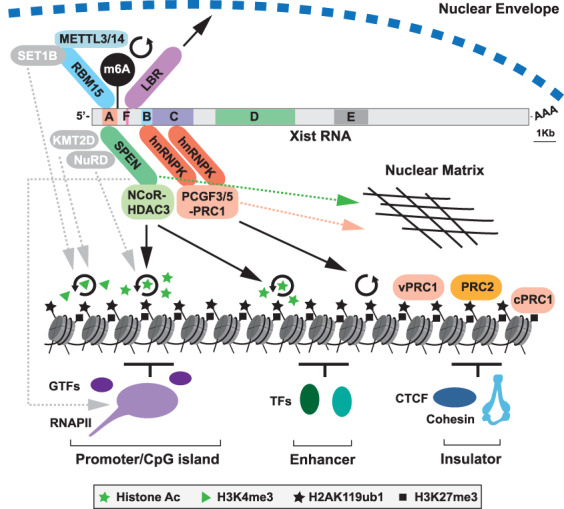
Pathways for Xist-mediated silencing. Schematic illustrates Xist RNA with tandem repeats A-F indicated together with associated RBPs and downstream effectors implicated in chromosome silencing. SPEN is linked to promoter/enhancer histone deacetylation through NCoR–HDAC3. hnRNPK recruits PCGF3/5–PRC1, which catalyzes widespread deposition of H2AK119ub1. H2AK119ub1 provides a binding platform for other variant (v) PRC1 complexes and PRC2, with PRC2-mediated H3K27me3, then recruiting canonical (c) PRC1. RBM15 is linked to m6A deposition on Xist RNA via recruitment of the METTL3/14 complex, facilitating silencing through yet to be determined mechanisms. LBR links Xist/Xi with the nuclear envelope and the repressive Lamin-associated environment. Other putative pathways, indicated in gray with dashed gray arrows, are RBM15-SET1B and/or SPEN–KMT2D potentially contributing to loss of H3K4me3 on Xi, SPEN–NuRD, potentially contributing to Xi histone deacetylation, and direct inhibitory interaction of SPEN with RNAPII/cofactors. Circular arrows denote catalytic activity. Both SPEN and PRC1 also contribute to anchoring Xist RNA to the nuclear matrix (dashed pink/green arrows), which may in turn contribute to their role in silencing.
