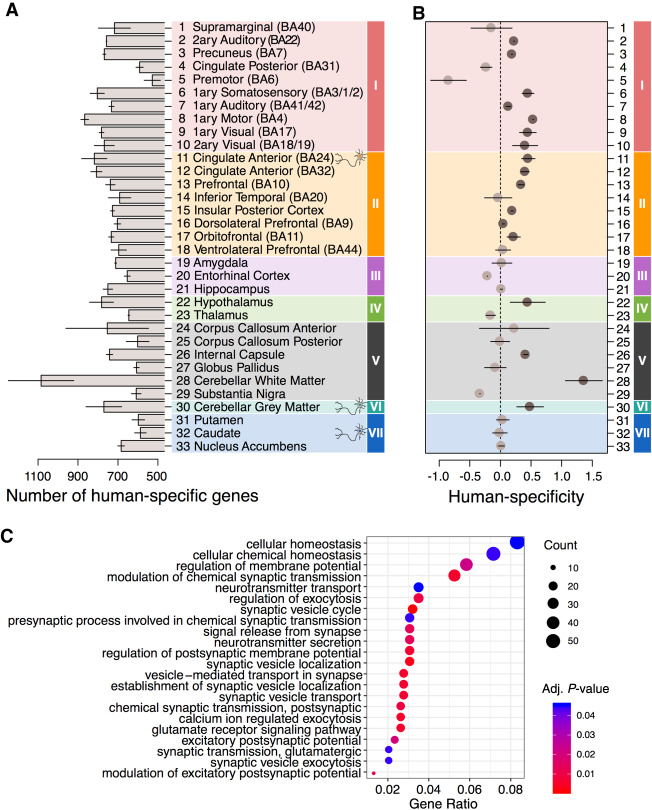
Figure 2.
Region-dependent analysis of human-specific gene expression differences. (A) Numbers of genes showing human-specific expression differences in each brain region. The differences were defined as those showing twofold greater human-macaque expression difference relative to the chimpanzee-macaque or bonobo-macaque difference. The bars show the mean of the chimpanzee-based and bonobo-based comparisons. The error bars span the difference between chimpanzee-based and bonobo-based estimates. Colors represent expression-based clusters of brain regions defined in Figure 1G. (B) The human-specificity ratio of gene expression estimated in each brain region as the ratio of human-specific expression differences and chimpanzee-specific or bonobo-specific expression differences. Circles show the mean of chimpanzee-based and bonobo-based comparisons, and lines span the difference between the two estimates. Darker circles mark brain regions showing an excess of human-specific expression differences compared to both ape species. (C) Top Gene Ontology (GO) functional terms enriched in the human-specific expression differences present in more than 10 of the 33 brain regions. The size of circles reflects the proportion of genes within the GO term among genes detected in the brain region using snRNA-seq data (Gene Ratio) (Yu et al. 2012). The color of circles indicates the BH-adjusted enrichment P-value.