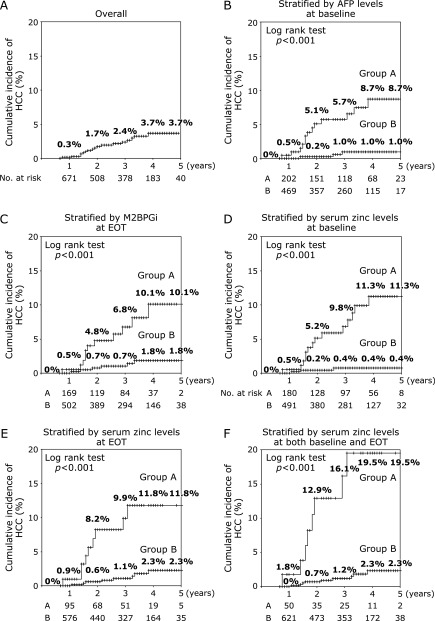
Fig. 3.
The cumulative rate of HCC by Kaplan-Meier analysis. AFP, α-fetoprotein; EOT, end of treatment; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; M2BPGi, Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer. (A) Overall cumulative incidence of HCC. (B) Cumulative incidence of HCC stratified by AFP at baseline. Group A (n = 220); baseline-AFP ≥6.0 ng/ml, Group B (n = 549); baseline-AFP <6.0 ng/ml (log-rank test p<0.001). (C) Cumulative incidence of HCC stratified by M2BPGi at EOT. Group A (n = 194); EOT-M2BPGi ≥2.5, Group B (n = 575); EOT-M2BPGi <2.5 (log-rank test p<0.001). (D) Cumulative incidence of HCC stratified by serum zinc levels at baseline. Group A (n = 197); baseline-serum zinc levels <60 µg/dl, Group B (n = 572); baseline-serum zinc levels ≥60 µg/dl (log-rank test p<0.001). (E) Cumulative incidence of HCC stratified by serum zinc at EOT. Group A (n = 107); EOT <63 µg/dl, Group B (n = 662); EOT ≥63 µg/dl (log-rank test p<0.001). (F) Cumulative incidence of HCC stratified by serum zinc at both baseline and EOT. Group A (n = 58); baseline-serum zinc levels <60 µg/dl and EOT-serum zinc levels <63 µg/dl, Group B (n = 711); baseline-serum zinc levels ≥60 µg/dl and/or EOT-serum zinc levels ≥63 µg/dl (log-rank test p<0.001).