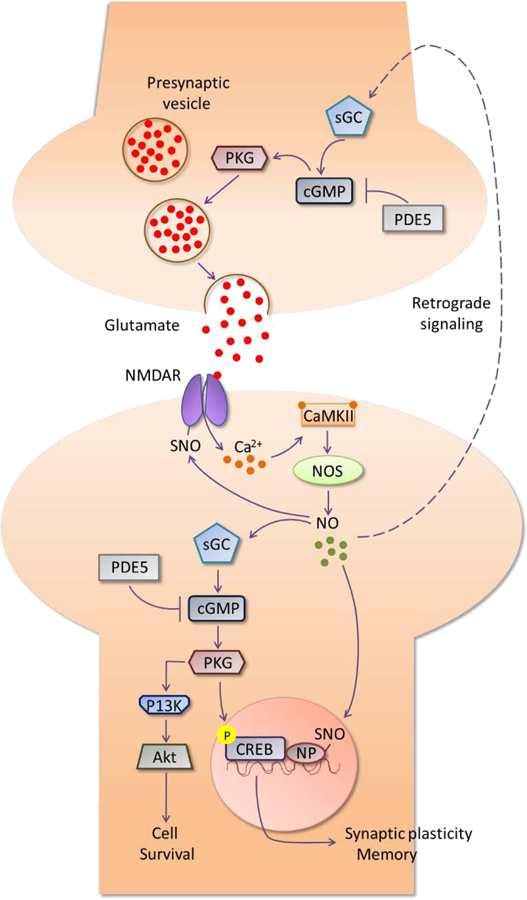
Figure 1.
Nitric oxide signaling pathway in the brain. NO, produced by NOS, binds to and activates sGC, which catalyzes the production of cGMP, a second messenger activator of PKG. Levels of cGMP are regulated by the cGMP-degrading enzyme PDE5. Finally, PKG phosphorylates CREB protein, an important transcription factor responsible for the expression of memory-related genes. An alternative route shows the activation of the PI3k/Akt signaling pathway by PKG, leading to the promotion of cell survival. S-nitrosylation of NP associated with CREB-binding genes facilitates the activation of CREB, while S-nitrosylation of NMDAR inhibits the receptor activity. At the presynaptic neurons, NO is involved in the retrograde signaling and promotes the release of neurotransmitters, like glutamate, after activation of the sGC/cGMP/PKG pathway. CaMKII: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate; CREB: cAMP response element-binding element; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; NO: nitric oxide; NOS: nitric oxide synthase; NP: nuclear proteins; PI3k: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PDE: phosphodiesterase; PKG: protein kinase G; SNO: S-nitrosothiol; sGC: soluble guanylate cyclase.