Figure 2.
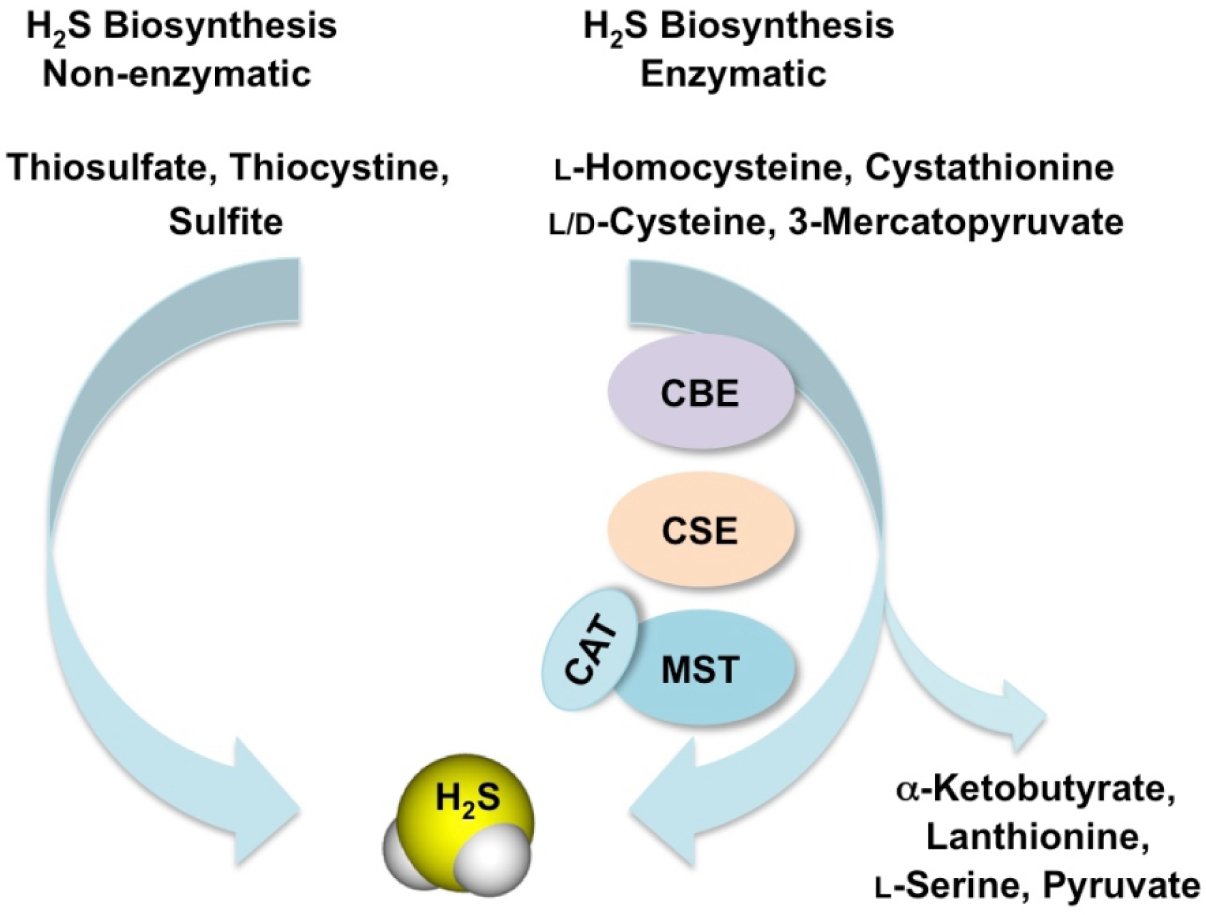
Biosynthesis of hydrogen sulfide. H2S is generated from oxidation of the substrates l-homocysteine, cystathionine, l-cysteine and 3-mercaptopyruvate through the enzymes cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) and the tandem enzymes cysteine aminotransferase (CAT) and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST). α-Ketobutyrate, lanthionine, L-serine and pyruvate are the secondary products formed. Mammalian enzymes generally metabolize l-amino acids, however, H2S can also be synthesized from d-cysteine by the peroxisomal enzyme d-amino acid oxidase (DAO) to 3-MP, which is a substrate for 3-MST. Alternatively, production of H2S occurs non-enzymatically from various storage forms of sulfur such as thiosulfate, thiocysteine and sulfite.
