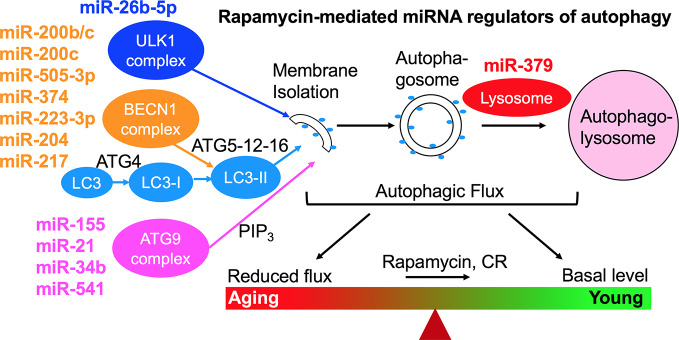
Figure 1.
Rapamycin-induced cardiac miRNA regulation of autophagy machinery. Since these same miRNAs are also differentially expressed in response to diabetes, this autophagy-inhibiting miRNA network is an inherent cardiac mechanism in response to conditions that induce activation of autophagy. This autophagy-inhibiting miRNA network may be an adaptive mechanism to prevent excessive autophagy that leads to cardiomyopathy and heart failure, or a detrimental mechanism that prevents autophagy progression and promotes cardiac senescence. It is important to note that careful monitoring of this autophagy regulation by determining changes in cardiac autophagic flux is a critical step in evaluating whether a longevity drug- or life style-induced increase in induction of autophagy is progressing appropriately to protect the heart tissue. New non-invasive imaging approaches need to be developed to couple cardiac autophagy progression with cardiac function.