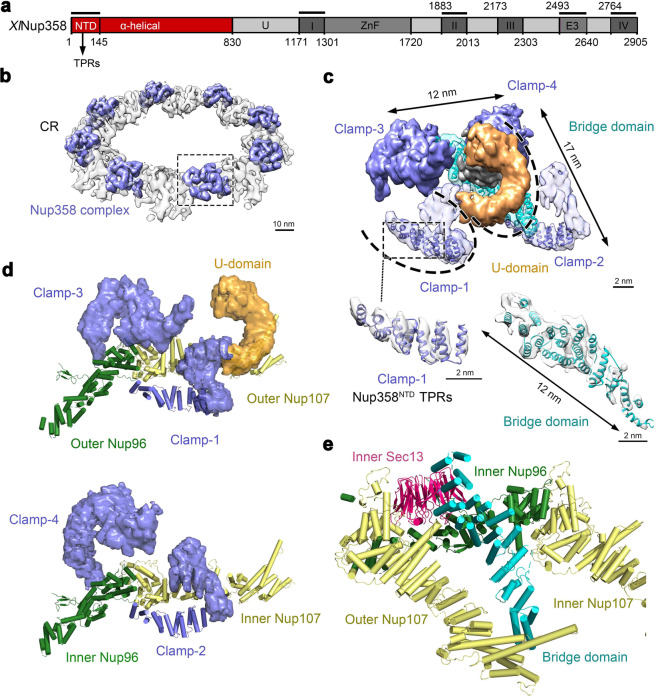
Fig. 4. Four Clamps of the Nup358 complex sandwich the stems of the inner and outer Y complexes.
a Domain organization of Nup358 from X. laevis (XlNup358). The various domains are drawn to scale. The thick black lines above the domain organization denote the fragments that have X-ray structures. In particular, the N-terminal domain (NTD, residue 1–145) of human Nup358 contains three TPRs (each encompassing a pair of α-helices).32 b The Nup358 complexes associate with the stems of the inner and outer Y complexes. Shown here is a cryo-EM reconstruction of the CR (transparent gray), with the Nup358 complexes shown in purple blue. c Structural features of the Nup358 complex. The Nup358 complex consists of four Clamps (Clamp-1, -2, -3, and -4, colored purple blue), and a bridge domain (cyan) in the center of the four Clamps. The ω-shaped Clamp-1 contains two U-domains, of which the second (orange) is out of plane with the first U-domain by nearly 90 degrees. The N-terminal 200-residue α-helices of Nup358 were modeled in Clamp-1 and -2. The bridge domain of 23 α-helices closely interacts with Clamp-4. The EM density maps for the N-terminal helices of Clamp-1 and the bridge domain are shown in the lower panels. d The Nup358 complex clamps the stem of the Y complex. Clamp-1 and Clamp-3 act like a pair of tweezers to hold the stem of the outer Y complex (upper panel). Similarly, Clamp-2 and Clamp-4 constitute a second pair of tweezers to hold the inner Y complex (lower panel). e The bridge domain of the Nup358 complex directly contacts inner Sec13, inner Nup96, and the finger helix of outer Nup107.