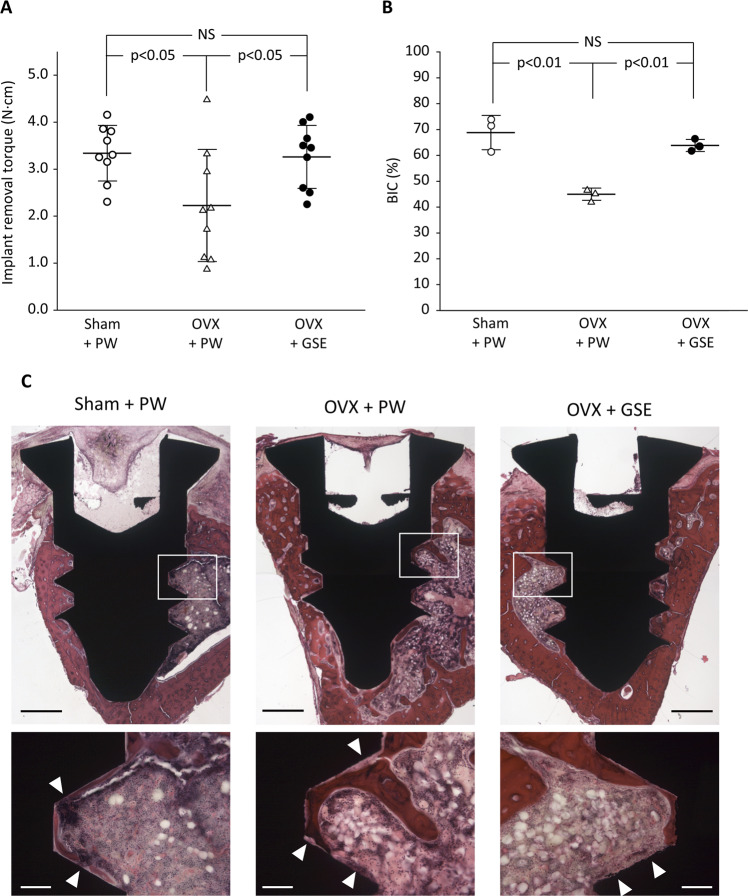
Figure 9.
Biomechanical and histological evaluation of implant osseointegration in ovariectomized (OVX) rats administered with proanthocyanidin-rich grape seed extract (GSE). (A) Removal torque (N⋅cm) of titanium screw-shaped implant installed in the tibia. Oral administration of GSE resulted in a significantly higher removal torque than did administration of pure water (PW) in OVX rats, whereas GSE did not significantly affect the implant removal torque in sham-operated (Sham) rats. The results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation, showing individual data (n = 9). (B) Quantification of bone-to-implant contact (BIC) percentage in each group. The results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation, showing individual data (n = 3). (C) Representative histological images of implants in Sham + PW, OVX + PW, and OVX + GSE groups obtained at low and high magnifications. The low magnification images are composite views generated based on the images obtained using a 5× objective lens. The high magnification images were obtained using a 20× objective lens, which correspond to the white square area in the low magnification images. White triangles in the high magnification images indicate the part where bone does not directly contact the implant surface. Scale bars in the low and high magnification images represent 500 and 100 µm, respectively.