Fig. 1.
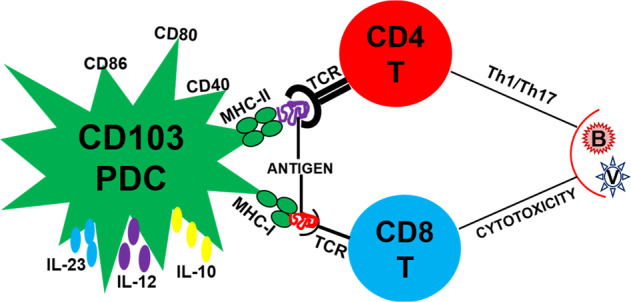
CD103+ PDC-mediated T-cell responses to pathogens. Following a respiratory infection with pathogens, CD103+ PDCs acquire and process microbial antigens, express costimulatory molecules (e.g., CD80, CD86, and CD40), secrete multiple cytokines (e.g., IL-23, IL-12, and IL-10), and migrate to the lung-draining lymph nodes to present the antigens on MHC-I/MHC-II molecules to the TCR of naive CD8+/CD4+ T cells, inducing cytotoxic/T helper (Th1/17) responses against viral and bacterial pathogens. PDC pulmonary dendritic cell, IL Interleukin, MHC major histocompatibility complex, TCR T-cell receptor, B bacterium, V virus
