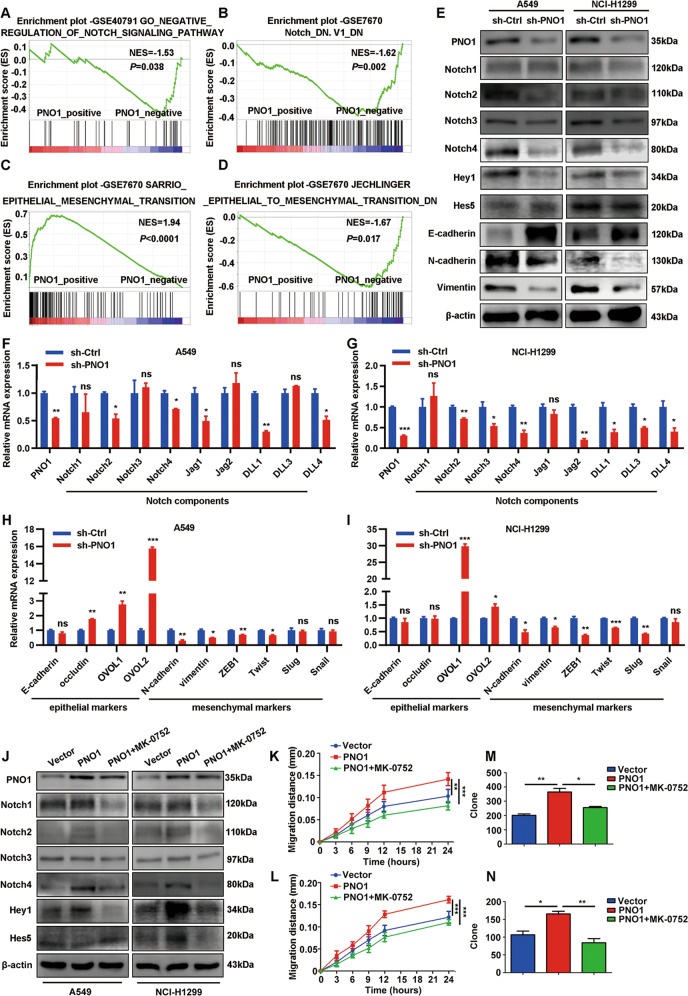
Fig. 5. Downregulation of PNO1 inhibits LUAD progression through Notch pathway and EMT.
a, b GSEA showed the relationship between the expression of PNO1 and Notch signaling pathway. c, d The correlation of PNO1 with EMT was investigated by GSEA analysis on the basis of GSE7670 datasets. e The protein level of each Notch intracellular domain, Notch target genes or EMT markers (such as Notch1-4, Hey1, Hes5, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and Vimentin) was assessed in sh-Ctrl and sh-PNO1 groups by Western Blotting. f, g The expression of Notch components (such as Notch2, Notch4, DLL1, and DLL4) was downregulated in sh-PNO1 groups of A549 or NCI-H299 cells by RT-PCR assay. h, i Epithelia-associated transcription factors (such as OVOL1 and OVOL2) expression was upregulated and mesenchymal-associated transcription factors (such as N-cadherin, vimentin, ZEB1, and Twist) expression was downregulated in the sh-PNO1 groups of A549 and NCI-H1299 by RT-PCR assay. j The protein level of each Notch intracellular domain and Notch target genes (such as Notch1-4, Hey1, and Hes5) was assessed in Vector, PNO1 or PNO1 + MK-0752 groups by Western Blotting. k, l The migration potential detected by wound-healing assay in Vector, PNO1 or PNO1 + MK-0752 groups. m, n The proliferation potential detected by colony formation assay in Vector, PNO1 or PNO1 + MK-0752 groups. nsP > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.