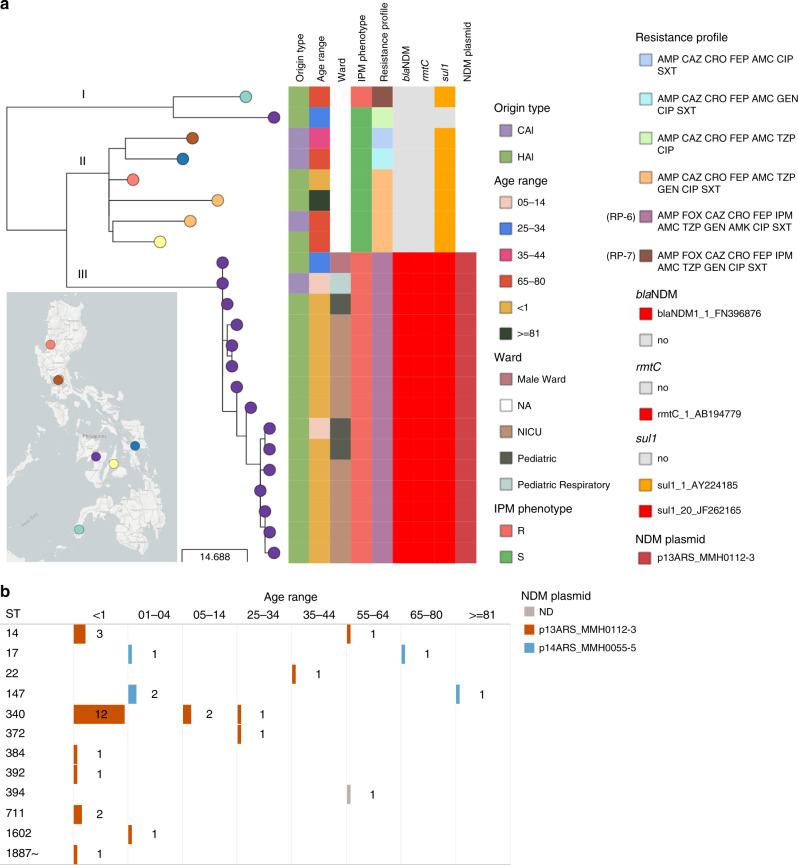
Fig. 4. Detection of a plasmid-driven outbreak of K. pneumoniae ST340.
a Phylogenetic tree and linked epidemiological and genotypic data of 24 retrospective ST340 genomes. Origin type defined as either community-acquired infection (CAI) or hospital-acquired infection (HAI). NA ward information not available. The imipenem (IPM) phenotype was either resistant (R) or susceptible (S). The three-letter antibiotic codes in the resistance profiles are as in Table 1. This interactive view is available at https://microreact.org/project/ARSP_KPN_ST340_2013-14/ac2a0920. The maximum-likelihood tree was inferred from 196 SNP positions identified by mapping the genomes to reference CAV1217 (CP018676.1 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/CP018676.1]), and masking regions corresponding to mobile genetic elements and recombination. The scale bar shows the number of SNPs per variable site. The full data are available at https://microreact.org/project/ARSP_KPN_ST340_2013-14. b Distribution of 33 isolates from hospital MMH with resistance profile RP-6 by patient age group, sequence types (ST) and NDM plasmid. Short reads of the 33 isolates were mapped to the plasmid sequences and a match was counted when the reads covered at least 95% of the sequence length with at least 5× depth of coverage. ND not detected.