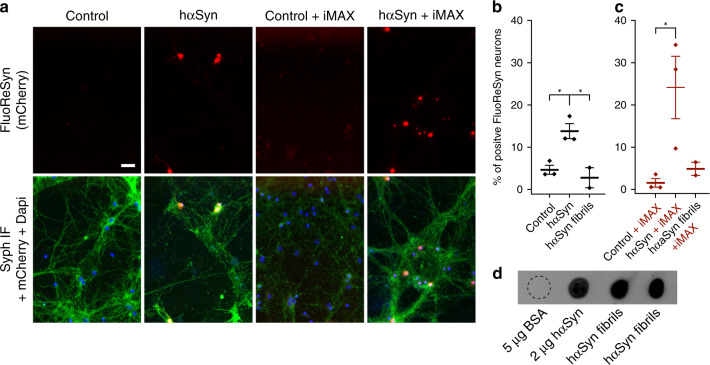
Fig. 6. Detection of hαSyn monomers added to the medium of cultured neurons.
a Equally scaled, representative images of primary rat hippocampal neurons infected with adeno-associated virus (AAV) encoding for NbSyn87-mCherry-NLS (a red version of the FluoReSyn). The cultures were then exposed to 20 µm of monomeric hαSyn, with or without RNAiMAX (iMAX), for 14 h. Immunofluorescence against synaptophysin was used as a neuronal marker (Syph IF, green signal). The negative controls were neurons receiving Opti-MEM with or without RNAiMAX. Scale bar represents 20 µm. b, c Quantification of FluoReSyn signal-positive neurons. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparison Tukey test *p < 0.05. Error bars represent the SEM, each point in the scatter plot represents the average of an independent experiment d Monomeric untagged hαSyn and two different batches of in vitro produced hαSyn fibrils were spotted on a nitrocellulose membrane and were detected by NbSyn87-Alexa647, which confirmed the ability of NbSyn87 to bind the fibrils used in hippocampal cultures. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used as negative control. Source data is available as a Source data file.