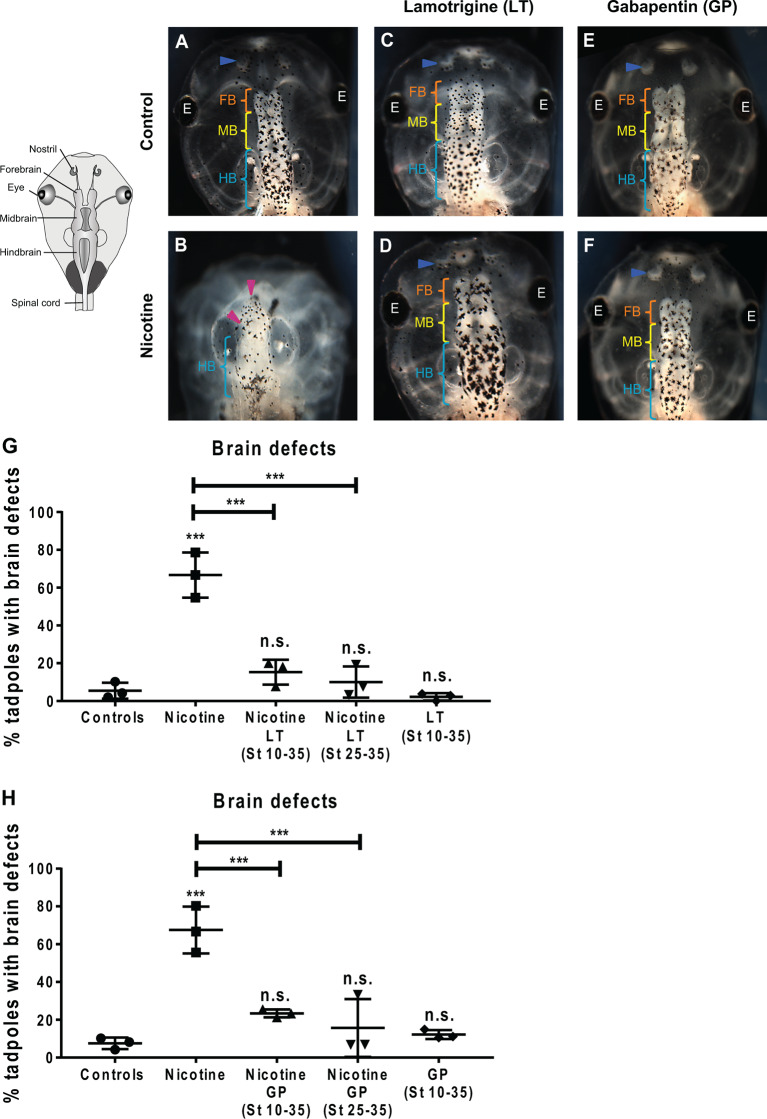
Figure 7.
Non-local exposure to Lamotrigine and Gabapentin (HCN channel agonist) rescues nicotine-induced brain morphology defects in Xenopus embryos. (A—F) Representative images of stage 45 tadpoles. Control (untreated and uninjected) or nicotine-treated tadpoles with or without treatment with lamotrigine (LT, stage 10–35) or gabapentin (GP, stage 10–35). Blue arrowheads indicate intact nostrils, orange brackets indicate intact forebrain (FB), yellow brackets indicate intact midbrain (MB), cyan brackets indicate intact hindbrain (HB), and magenta arrowheads indicate severe brain morphology defects. (G,H) Quantification of stage 45 tadpole brain morphology defects under the indicated conditions for lamotrigine (LT; G) or gabapentin (GP; H). Percentage of tadpoles with brain defects for each experimental group are: (G) Controls—5%, Nicotine—67%, Nicotine+LT (St10–35)—15%, Nicotine+LT (St25–35)—10%, and LT(St 10–35)—2%; (H) Controls—7%, Nicotine—68%, Nicotine+GP (St10–35)—23%, Nicotine+GP(St25–35)—16%, and GP(St 10–35)—11%. Data are mean ± SD, ***p < 0.001, n.s.: non-significant (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for n = 3 independent experiments with N > 50 embryos per treatment group per experiment).