FIGURE 2.
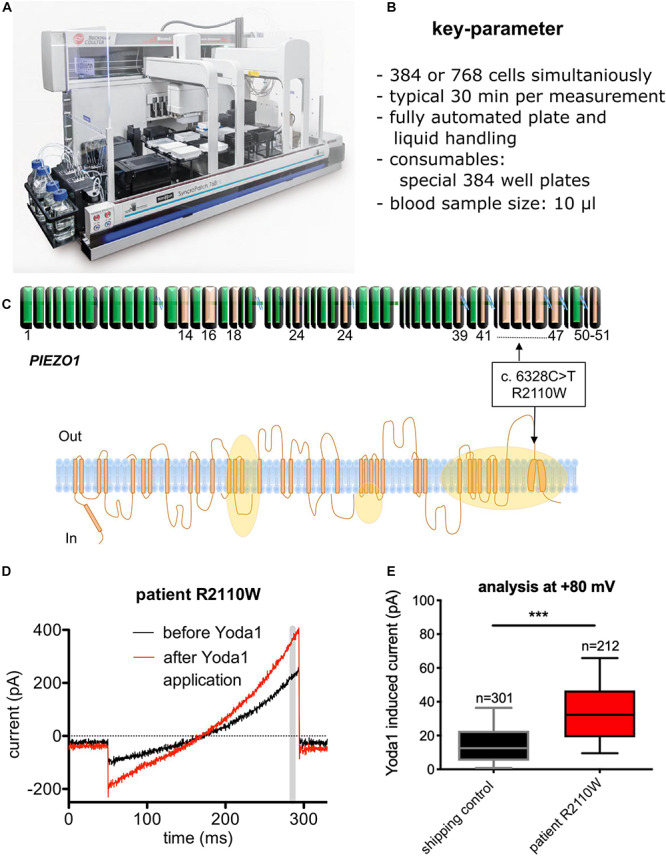
Diagnosis of a novel PIEZO mutation with automated patch-clamp technology. (A) Image of the SyncroPatch device (Nanion Technologies, Munich, Germany). (B) List of key parameters of the SyncroPatch. (C) Illustration of a novel mutation (R2110W) of the Piezo 1 ion channel. Although detected per se, it was unknown if the mutation has a functional effect on the red blood cells. Orange areas represent regions affected by previously reported mutations. (D) Raw data traces of a red blood cell recording for illustration. Yoda1 is a specific activator of Piezo 1. The gray bar depicts the time point (= membrane potential), which was used for the statistical analysis. (E) Statistical analysis of all measured cells (R2110W mutation vs. control) to exemplify the functional impact of the mutation. n gives the number of successful measured and analyzed cells. (A) Reproduced with permission from Nanion Technologies. (C–E) Reproduced from Rotordam et al. (2019) with permission of the Ferrata Storti Foundation.
