Figure 1.
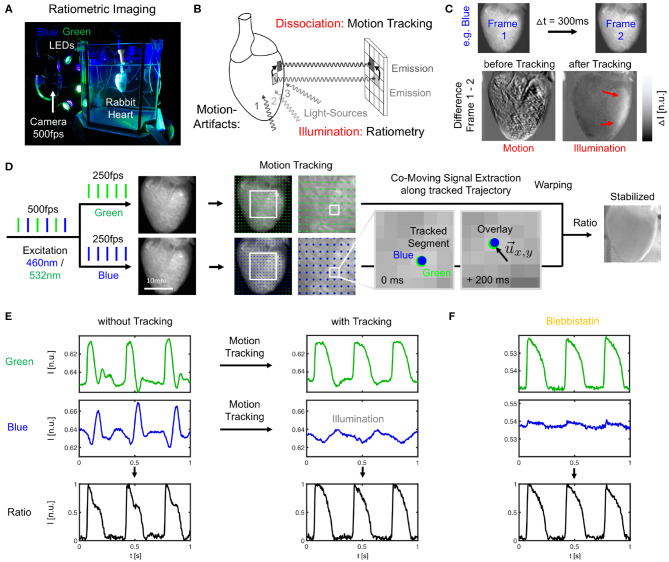
Dual-channel ratiometric optical mapping in combination with marker-free numerical motion tracking and motion-stabilization for imaging action potential waves on the contracting surface of isolated hearts. (A) Ex-vivo optical mapping setup with a single camera. (B) Sources for motion artifacts: dissociation-related and illumination-related motion artifacts are compensated with motion tracking and ratiometry, respectively. (C) Two types of motion artifacts visible when computing the difference between video frames. Before tracking, motion creates dissociation-related motion artifacts. After tracking, relative motion between heart surface and light sources (which now move in motion-stabilized video) causes residual intensity fluctuations or illumination-related motion artifacts (red arrows). (D) Imaging scheme with alternating blue (460 nm) and green (523 nm) illumination for excitation of Di-4-ANEPPS and exposure of consecutive video frames at 2 × 250 or 500 fps. Separate motion tracking in each channel (every n-th displacement vector shown, shifts are tracked in every pixel). Overlay of tissue coordinates tracked in blue and green channel, respectively, shows congruent motion through the video images, see also Supplementary Video 1. Combination of warped green and blue video images yields motion-stabilized ratiometric video image. (E) Optical traces (from 3 × 3 pixels) before and after tracking and/or ratiometry (pacing CL = 350 ms) in blue and green (inverted) channel, respectively. Ratiometry alone cannot completely remove all motion artifacts (bottom left), but only illumination-related motion artifacts. Numerical motion-stabilization alone cannot completely inhibit all motion artifacts (top right), but only dissociation-related motion artifacts. After tracking, ratiometric combination of green and blue signals yields an optical signal with very little residual motion artifacts. Due to the particular dye and filter properties, the relevant electrophysiological signal is in the green channel, whereas eventual intensity fluctuations in the blue channel (after tracking) are caused mostly by motion through an inhomogeneously illuminated scene. (F) Optical traces obtained with Blebbistatin in same heart. Ratiometry improves the signal with very little residual contractile motion, or after numerical motion-stabilization as in (E).