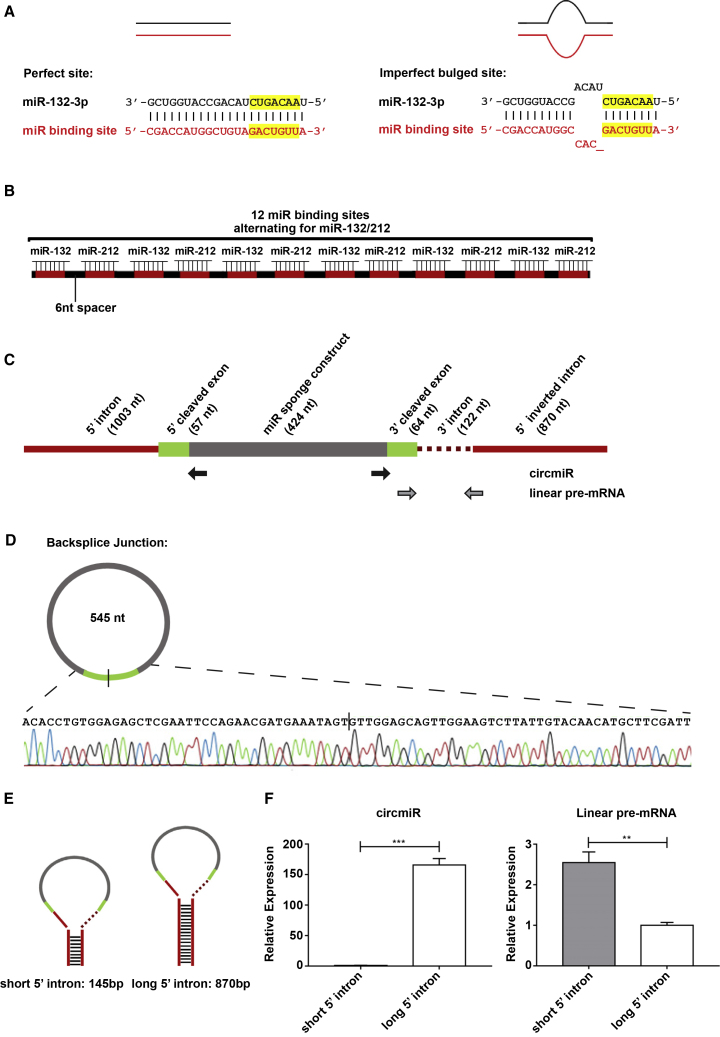
Figure 1.
Engineering of a Circular miRNA Sponge
(A) Design of a perfect complementary or imperfect bulged miRNA binding site. The bulge is created by one base deletion and three base mismatches at positions 9–12 nt. Seed regions are highlighted in yellow. (B) Schematic illustration of miRNA sponge construct carrying 12 binding sites separated by 6 nt spacers. (C) Schematic illustration of circmiR expression construct, indicating positions of the convergent (gray arrows) and circmiR-specific divergent (black arrows) PCR primer binding sites. (D) Sanger sequencing of PCR product following amplification with divergent circmiR primers confirming back-splicing of the miRNA sponge construct. (E) Schematic of varying length of intronic sequences, short and long, flanking the miRNA sponge sequence. (F) Expression abundance of circRNA derived from constructs with short or long flanking intronic sequences in transfected HEK293T cells using qPCR. (n = 3); ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Student’s t test.