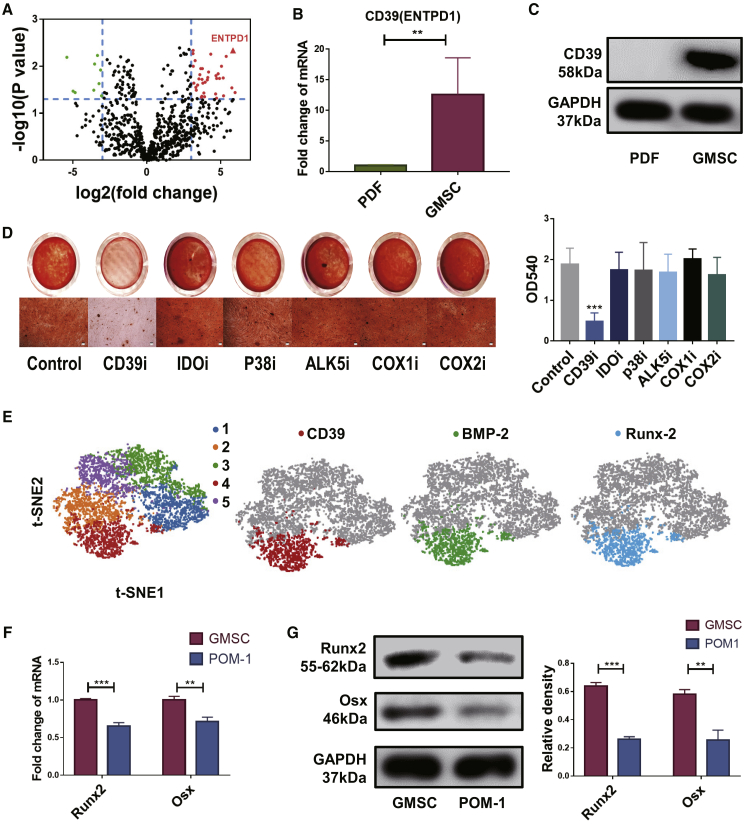
Figure 3.
Osteogenic Function of GMSCs Depends on CD39
Gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells (GMSCs) and prepuce-derived fibroblasts (PDFs) derived from three different individuals. Fresh cells or resuscitated stored cells from the third to the fifth passages were used in the experiments. (A) RNA sequence volcano map for GMSCs and control cell PDFs. (B) qPCR result showing the CD39 expression levels of the GMSCs and PDFs, n = 3. (C) Western blotting of the CD39 levels of the GMSCs and PDFs, n = 3. (D) GMSCs were pretreated with CD39 inhibitor (POM-1, 100 μM), IDO inhibitor (1-MT, 500 μM), p38 inhibitor (SB203580, 10 μM), ALK5 inhibitor (10 μg/mL), selective cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1) inhibitor (indomethacine, 20 μM), and selective COX-2 inhibitor (NS-398, 20 μM) overnight; then induced osteogenesis followed with alizarin red staining. Representative gross look and image under microscope were shown under different conditions and the quantification by hexadecyl pyridinium chloride monohydrate in different treatment groups, n = 3. (E) Five GMSC clusters, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) of GMSCs, colored by clustering. CD39, BMP-2, and Runx2 expression in single-cell sequence clusters. (F) qPCR result showing genes related to osteoblast formation and development expression on GMSCs and POM-1-pretreated GMSCs, n = 3. (G) Runx2 and Osx expression on GMSCs and POM-1-pretreated GMSCs was determined using western blotting. The relative density to GAPDH was shown, n = 3. The results represent three independent experiments (mean ± SEM), ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by Mann-Whitney tests or t test or ANOVA test.