Figure 4.
Recognition of Reporter Antigens by the Immune System
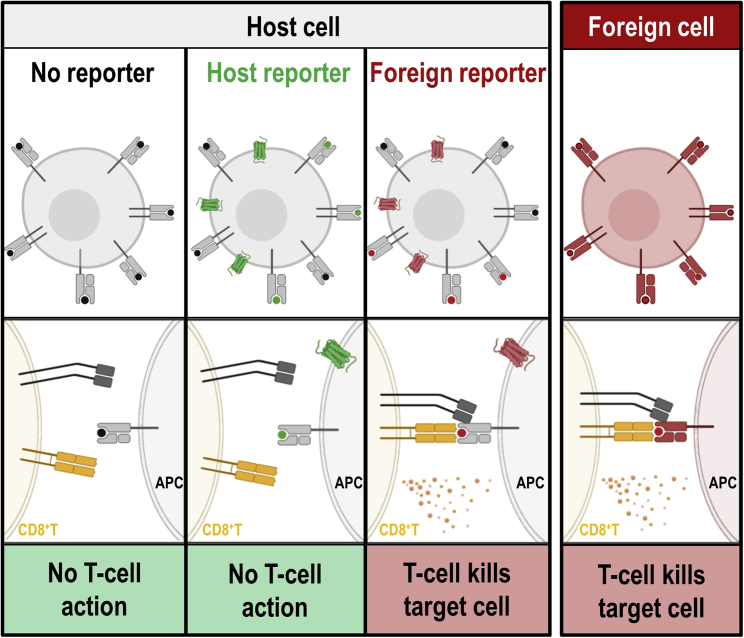
The intact mammalian immune system operates several mechanisms to recognize cells expressing non-self (i.e., non-host) proteins. As one simplified example, we show here the recognition of antigen-presenting MHC class I molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) by cytotoxic T cells (CD8+Ts). Host cells (far left column, black dots representing presented host antigens) are not recognized by CD8+Ts, as they are pre-coded to not target self. In contrast, non-self MHC class I molecules on foreign cells (far right column) are recognized by CD8+Ts, resulting in destruction of the foreign cells. If host cells express host reporters (center left column, green), corresponding host antigens (green dots) can be presented on MHC class I molecules, and as they are representing self CD8+Ts take no action when they encounter these cells. If foreign reporters are expressed (center right column), self MHC class I molecules present non-self/foreign antigens (red dots), resulting in CD8+T action and killing of the corresponding host cell due to the presence of the foreign reporter. The figure was generated using Biorender.com.