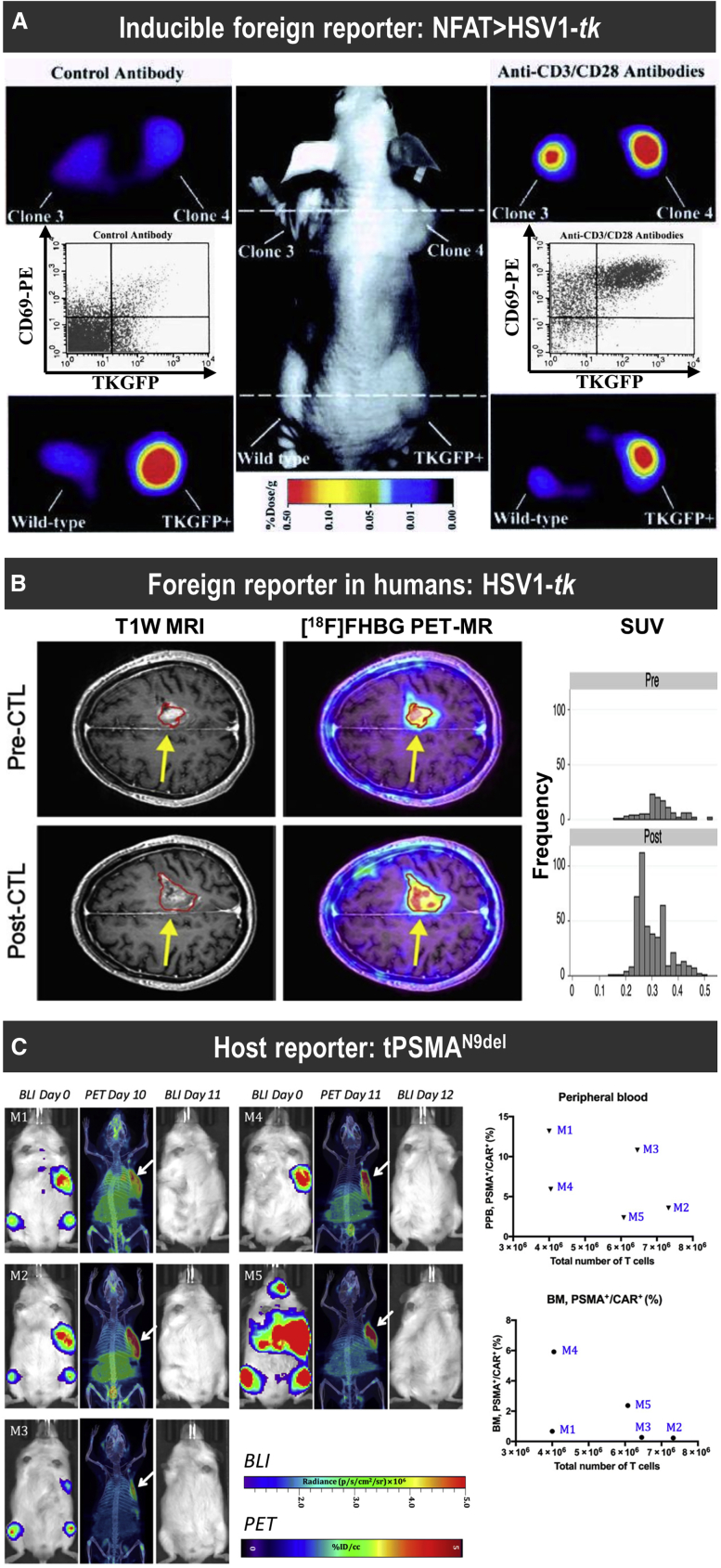
Figure 5.
Examples of Foreign and Host Reporters for T Cell Tracking
(A) Proof-of-principle study demonstrating non-invasive imaging of T cell activation by NFAT-driven expression of the reporters HSV1-tk and GFP (TKGFP) with [124I]FIAU as a PET radiotracer for HSV1-tk. Photographic image of a typical mouse bearing different subcutaneous infiltrates (middle panel); transaxial PET images of TKGFP expression in a mouse treated with control antibody (left panels) and T cell-activating anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies (right panels) were obtained at the levels indicated by the dashed lines of the middle panel. Samples are the Jurkat/dcmNFATtgn clones 3 and 4 (two similar clones), wild-type Jurkat infiltrates (no reporter control), and Jurkat/TKGFP (constitutive reporter expression as positive control). Gray inset plots show fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) profiles for reporter expression (TKGFP) versus a T cell activation marker (CD69) from a tissue sample obtained from the same Jurkat/dcmNFATtgn clone 4 infiltrate that was imaged with PET above. (B) [18F]FHBG PET was performed in a 60-year-old male with multifocal left hemispheric glioma, who received cytotoxic T lymphocytes into the medial left frontal lobe tumor (yellow arrows). Tumor size was monitored by T1-weighted contrast-enhanced MRI (left panels). [18F]FHBG PET to detect HSV1-tk was recorded and images were fused with MR images (right panels), and 3D volumes of interest were drawn using a 50% [18F]FHBG maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) threshold, outlined in red. Top row: Images and voxel-wise analysis of [18F]FHBG total radioactivity prior to CTL infusion and (bottom row) 1 week after CTL infusion.155 (C) Longitudinal imaging CAR-T tracking study demonstrating that the number of CD19-tPSMAN9del CAR-T cells in the peripheral blood and the bone marrow does not correlate with the total number of the CD19-tPSMAN9del CAR-Ts localized to the tumors. Left: PET/CT and BLI images of five different mice. Days are marked from the day of CAR-T infusion. Mice were imaged on a SuperArgus small-animal PET/CT 1 h after administration of 14.8 MBq of [18F]DCFPyL. Images alternate between fLuc-tagged bioluminescence (BLI, radiance) for visualization of tumor cells and PET/CT for CAR-Ts, with each mouse undergoing both imaging studies. Arrows designate accumulation of CAR-Ts. To improve the display contrast of the in vivo images, the relatively high renal radiotracer uptake was masked using a thresholding method. Images are scaled to the same maximum value within each modality. Right: Quantified numbers of the CD19-tPSMAN9del CAR-Ts in the region of interest drawn to cover the entire tumor area were plotted with the percentage number of PSMA+/CAR+ cell populations in the peripheral blood (PPB) and the bone marrow (BM). Each data point (M) represents each mouse. For details, see Minn et al.29 [Figure modified from publications cited above with permissions obtained.]