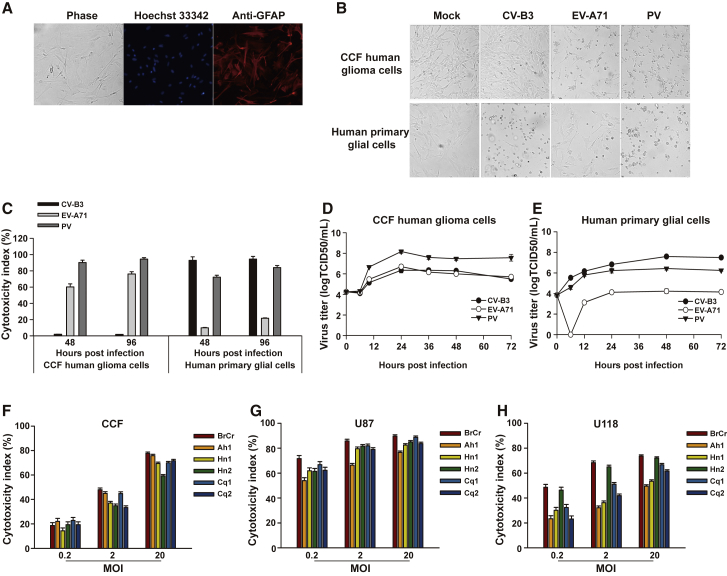
Figure 1.
Cytolytic Properties of EVs against Human Glioma Cells
(A) Human NPCs differentiated for 21 days down a glial pathway resulted in staining for the astrocytic marker GFAP (red) by approximately 95% of all cells. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). Magnification, ×100. The results of one representative experiment out of three are shown. (B) Human CCF glioma cells and normal glial cells were infected with either CV-B3 Nancy, EV-A71 BrCr, or PV-1 Sabin (MOI = 1) for 48 h. Representative images were acquired under a phase-contrast microscope (magnification, ×100). (C) Human CCF glioma cells and normal glial cells were challenged with EVs (MOI = 1) for 48 h or 96 h. Cell supernatants were assessed to measure cytotoxicity. (D and E) Human CCF glioma cells (D) and normal glial cells (E) were challenged with EVs at an MOI of 1. At various times after infection, the virus titers in the culture were determined by the TCID50 assay. (F–H) EV-A71 killing of glioma cells. Three glioma cell lines, CCF (F), U87 (G), and U118 (H), were separately infected with six EV-A71 strains (BrCr, Henan1 [Hn1], Henan2 [Hn2], Chongqing1 [Cq1], Chongqing2 [Cq2], and Anhui1 [Ah1]) at MOIs of 0.2, 2, or 20 for 48 h. Cytotoxicity was assessed by an LDH assay. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviations obtained from three independent experiments.