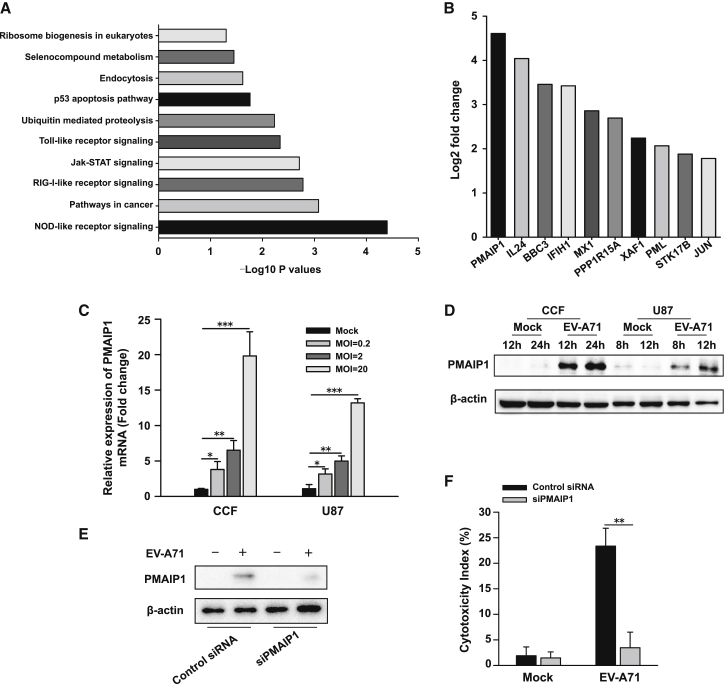
Figure 3.
PMAIP1 Induction Is Involved in EV-A71-Mediated Oncolysis
(A) RNA-seq analyses of EV-A71-infected and mock-infected human glioma cells. Genes with significant differences in expression were subjected to GO analyses. The typical 10 most significant terms are shown. The −log10 p values are indicated by bar plots. (B) RNA expression analysis of RNA-seq results. Bar plots indicate induction of apoptosis-related genes in EV-A71-infected glioma cells, as compared with mock cells. (C and D) EV-A71 increases PMAIP1 mRNA and protein levels in human glioma cells. Total RNA and whole-cell lysates were prepared from CCF or U87 cells treated with EV-A71 BrCr or vehicle as control. (C) PMAIP1 mRNA expression was quantified by real-time PCR, 6 h after virus treatment with the indicated MOIs. (D) Immunoblot analysis was performed for PMAIP1 protein expression after treatment with EV-A71 at an MOI of 2 for indicated times. beta-actin was used as control for protein loading. One representative image of three experiments is shown. (E and F) Knockdown of PMAIP1 reduces EV-A71-mediated oncolysis. U87 glioma cells were treated with siRNA for 48 h. Cells were then infected with EV-A71 (MOI = 2) for an additional 8 h. (E) Reduced NOXA expression was confirmed by immunoblotting. (F) EV-A71-induced oncolysis was measured by an LDH assay. Bars represent the mean ± the standard deviations of three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.