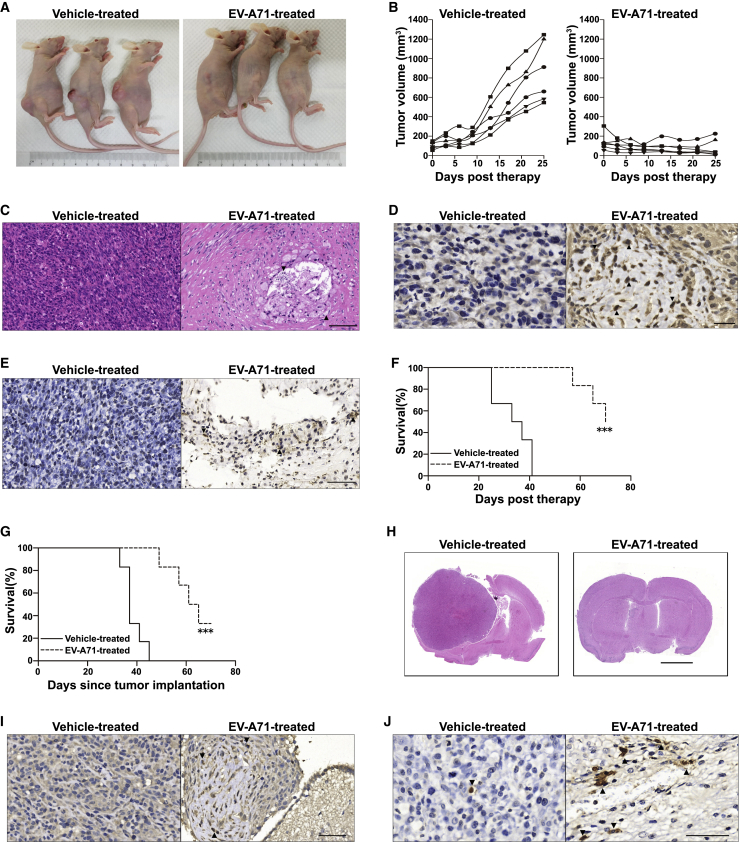
Figure 4.
EV-A71 Oncolytic Activity against Glioma Xenografts
(A and B) Nude mice bearing subcutaneous U87 tumors were treated with intratumoral injection of vehicle or EV-A71. (A) Representative photographs of the xenograft tumor on day 25 post-therapy are shown. (B) The tumor burden was monitored by calculating the tumor volume versus time using calipers. (C) Representative H&E staining of the remaining tumor mass at 25 days post-treatment with vehicle or EV-A71. Black triangles indicate significant tumor cell loss. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Representative IHC analysis of EV-A71 proteins in paraffin-embedded sections. Black triangles indicate positive staining for virus protein 2B. Scale bar, 20 μm. (E) Representative apoptosis analysis in vehicle- or EV-A71-treated subcutaneous glioma xenografts. Black triangles indicate significant features of apoptotic cell death. Scale bar, 50 μm. (F) Overall survival of mice was assessed using the Kaplan–Meier survival log rank test. The animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation once the implanted tumor size exceeded 15 mm in any direction, which was considered the humane endpoint of survival data. (G) Nude mice bearing intracranial U87 tumors were treated with intratumoral injection of vehicle or EV-A71 BrCr. Overall survival was analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier survival log rank test. (H) Representative coronal H&E-stained sections of nude mouse brains. The tumors of mock-treated moribund animals encompassed almost the entire hemisphere with marked hypercellularity, whereas only microscopic residual tumor cells remained in EV-A71-treated animals at the same time. Scale bar, 2 mm. (I) Representative IHC detection of EV-A71 protein 2B (marked with black triangles). Scale bar, 50 μm. (J) Representative apoptosis analysis in intracranial glioma xenografts as detected by TUNEL staining (marked with black triangles). Scale bar, 50 μm. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.