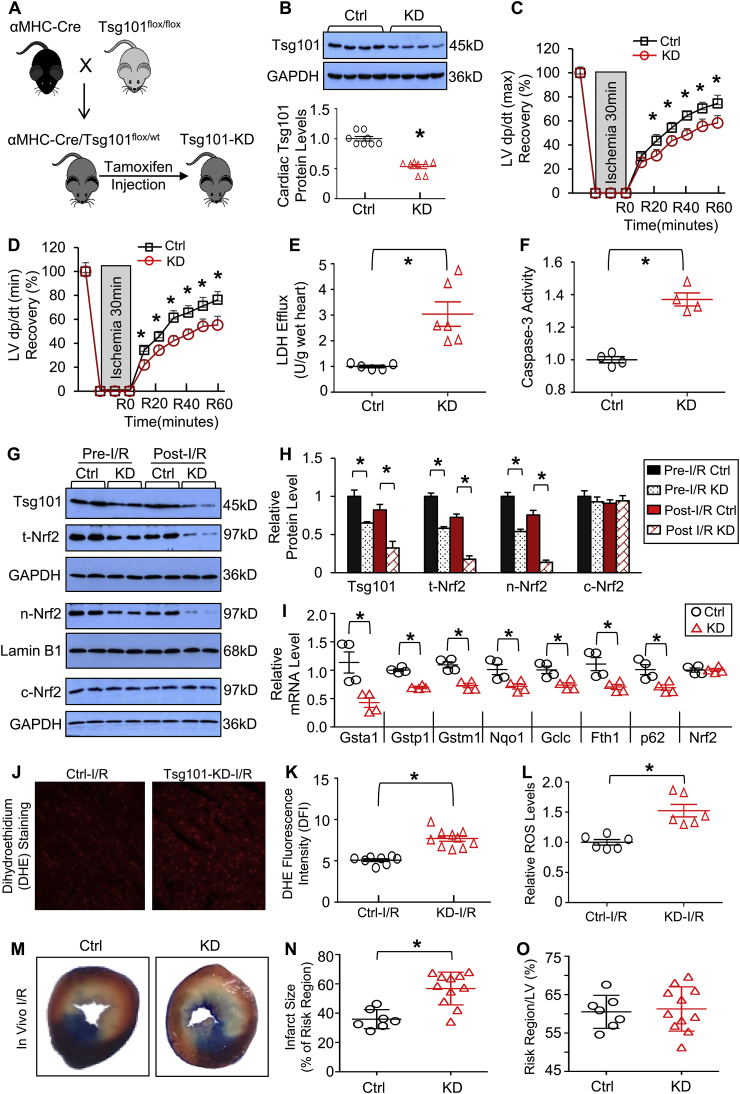
Fig. 5.
Knockdown of Tsg101 aggravates I/R-triggered cardiac dysfunction and ROS production. (A) Schematic diagram depicting the generation of inducible cardiac-specific Tsg101 knockdown (Tsg101-KD) mice (B6/129). (B) Representative Western-blots and quantification analyses showing Tsg101 protein levels in control (Ctrl: Cre−/Tsg101flox/wt littermates) and Tsg101-KD mouse hearts. *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl. (C/D) Tsg101-KD hearts demonstrated worse contractile function recovery during ex vivo I/R (30min/1 h), compared to controls. n = 6 for each group. *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl. (E) Total LDH levels in coronary effluent collected during the first 10 min of reperfusion. *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl. (F) Caspase-3 activity in Ctrl- and KD-hearts subjected to ex vivo I/R (30min/1 h), *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl. (G) Representative Western-blots and (H) quantification analysis showing the expression levels of Tsg101, total Nrf2, nuclear Nrf2 and cytosolic Nrf2 in pre-I/R and post-I/R hearts. *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl, n = 4. GAPDH was used as a loading control for total and cytosolic proteins, and Lamin B1 was used as a loading control for nuclear proteins. (I) mRNA levels of Nrf2 target genes in post-I/R hearts. *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl. (J) Representative images and (K) quantification analysis of DHE staining in sections from Ctrl- and KD-hearts subjected to ex vivo I/R (30min/5min). *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl-I/R. (L) ROS levels, measured by DCFH2M fluorescence intensity, in Ctrl- and KD-hearts subjected to ex vivo I/R (30min/5min). *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl-I/R. (M) Representative infarction images of mouse hearts upon in vivo I/R (30min/24 h) and (N) quantitative results of infarction size and (O) the ratio of risk region to left ventricular (LV) area. *, p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl.