Fig. 6.
Assessment of immunomodulatory activity of glycine‐induced EcNΔflhD MVs.
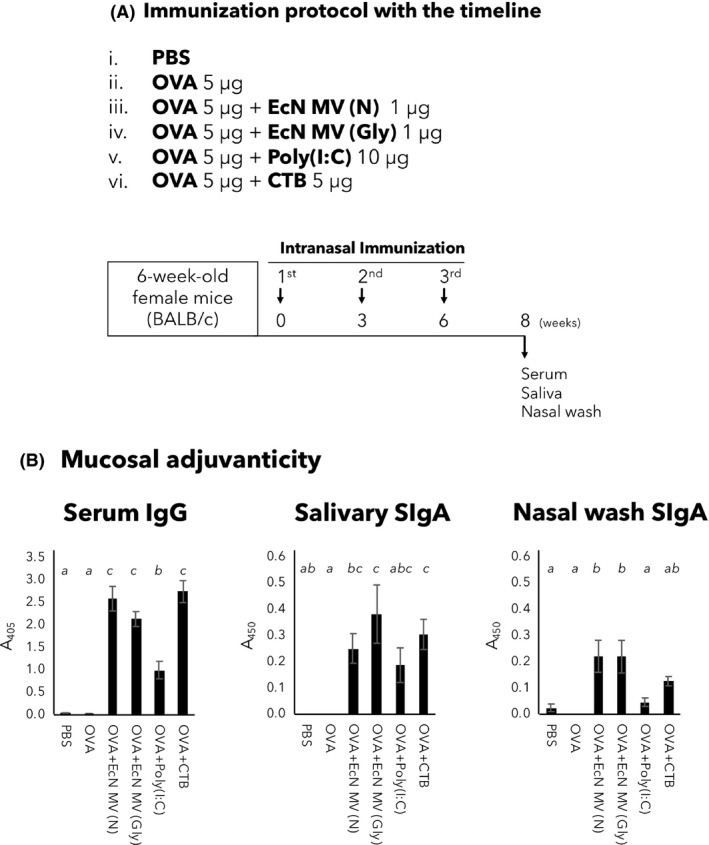
(A) Experimental design of intranasal vaccine model study using BALB/c mice. The mucosal adjuvanticity of glycine‐induced MVs was examined in this animal study. Female BALB/c mice aged 6 weeks were intranasally immunized three times with the following six conditions (n = 10 mice for each group): (i) PBS, mock immunization, (ii) OVA alone, (iii) OVA + non‐induced MVs (N), (iv) OVA + glycine‐induced MVs (Gly), (v) OVA + Poly(I:C) and (vi) OVA + CTB. At 14 days after the third vaccination, serum, saliva and nasal wash samples were collected from mice. ELISA was carried out to examine OVA‐specific serum IgG and IgA, salivary SIgA and nasal wash SIgA.
B. Mucosal adjuvanticity of glycine‐induced MVs. At two weeks after the third vaccination, serum, saliva and nasal wash samples were collected from mice intranasally immunized with the following six conditions (n = 10 mice for each group): (i) PBS, mock immunization, (ii) OVA alone, (iii) OVA + non‐induced MVs (N), (iv) OVA + glycine‐induced MVs (Gly), (v) OVA + Poly(I:C) and (vi) OVA + CTB. ELISA was carried out to examine OVA‐specific serum IgG, salivary SIgA and nasal wash SIgA. Shown are A405 or A450 (mean ± SE) values. Samples of serum, saliva and nasal wash were diluted to 1:100, and used as primary antibody of ELISA. All the values except serum IgG were obtained after 60‐min incubations with AP or HRP. The value of serum IgG was obtained after a 30 min of incubation with AP. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison test. Different alphabet superscripts indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).
