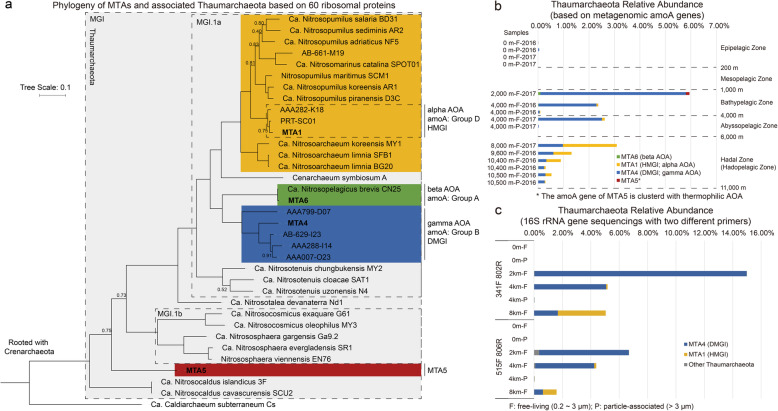
Fig. 1.
Diversity and distribution of Thaumarchaeota in the Challenger Deep, Mariana Trench. Clade classification is based on Massana et al. and Nunoura et al. [25, 28]. a Phylogenetic tree based on 60 ribosomal proteins (inferred amino acid tree). This is a maximum likelihood tree with Poisson model and universal rates on all sites. Sites presented in less than half of taxa were deleted. All branches gave 100% bootstrap support after 100 tests except where indicated with the values indicated next to the branch. There were 8602 positions in the final alignment. Ribosomal proteins used in this phylogenetic analysis are documented in Additional file 1: Table S7. b AOA relative abundance at various depths based on the ratio of the coverage of the amoA gene to the average of the single-copy marker genes in metagenomes. Alternative amoA gene-based classification is based on Francis et al. [18]. Abundance of the clades was estimated by calculating the amoA gene abundance from these clades directly in our environmental samples. Since MTA4 does not have the amoA gene due to its incompleteness, an amoA gene from the same clade (gamma AOA) was used instead. c AOA relative abundance at various depths based on 16S rRNA sequencing in 2017 samples. PCR primers used in the 16S rRNA sequencing are listed in Additional file 1: Table S6