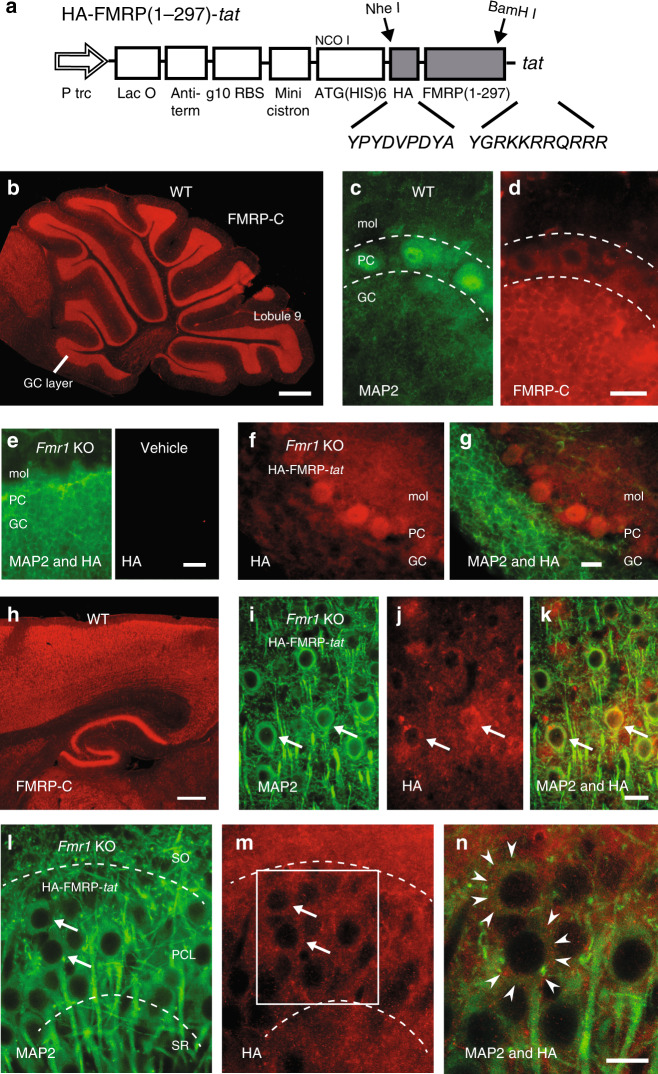
Fig. 4. A FMRP(1–297)-tat construct rapidly crosses the BBB to enter central neurons.
a Schematic diagram of HA-FMRP(1–297)-tat construct. HA sequence and 11 aa tat sequence were inserted through the two restriction enzyme sites indicated by arrows. b–d Immunolabel distribution for an FMRP C-terminus (FMRP-C) antibody in WT mouse cerebellum with expanded views of dual labeled MAP2 (c) and FMRP-C (d) in lobule 9 cell layers. e–g Cerebellar sections from Fmr1 KO mice that were tail vein injected with either vehicle (e) or 1.0 mg/kg HA-FMRP(1–297)-tat (f, g) and processed 30 min later for MAP2 and HA labeling. HA label is absent in vehicle-injected Fmr1 KO mouse cerebellum (e) but is detected in all cell layers after tail vein injection of HA-FMRP(1–297)-tat (f, g). h Low power view of immunolabel for the FMRP-C antibody in WT mouse in the region of neocortex and hippocampus. i–n Magnified views of Fmr1 KO mouse neocortex at 30 min (i–k) and CA3 hippocampus at 12 h (l–n) following tail vein injection of 1.0 mg/kg HA-FMRP(1–297)-tat and dual labeled for MAP2 and HA. Boxed region in (m) is magnified in (n), with the boundaries of cell membranes of hippocampal pyramidal cells denoted by arrowheads in (n) to distinguish FMRP(1-297) immunolabel in cytoplasmic regions. Dashed lines in (c, d) and (l, m) delineate major cell boundaries and arrows in (l, m) highlight representative cells exhibiting both MAP2 and HA immunolabels. Animals used for immunolabeling ranged from P25–P40, with immunolabel experiments conducted in at least 3 separate animals in (b–n). GC granule cell layer, PC Purkinje cell layer, mol molecular layer, SR stratum radiatum, PCL pyramidal cell layer, SO stratum oriens. Scale bars: b, h, 500 µm; c–g, i–n, 20 µm.