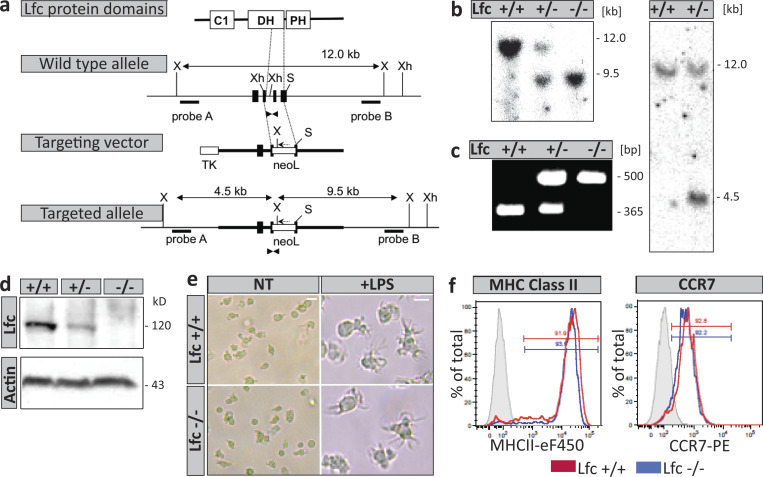
Figure S3.
Disruption of the Lfc gene locus. The targeting vector was constructed by substituting genomic DNA corresponding to the end of the Dbl homology (DH) domain and the interface between DH and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains with a LoxP-Neo-LoxP cassette in order to generate a null mutation. (a) Integration of the Lfc targeting vector into the genomic locus. Black boxes represent exons. The neo-LoxP (neoL) cassette was cloned in reverse orientation into two exons (one coding for the DH domain, the other for the DH/PH interface), replacing a SmaI-XhoI segment. Locations of primers used for PCR are indicated with triangles. Probes A and B were used for Southern blot detection of short and long arms, respectively. S, SmaI; Xh, XhoI; X, XbaI; DH, Dbl homology; PH, Pleckstrin homology. (b) Southern blot analysis. Left panel: Genomic DNA from Lfc+/+, Lfc+/−, and Lfc−/− mice was digested with XbaI and hybridized with probes B. Right panel: Genomic DNA from Lfc+/+ and Lfc+/− embryonic stem cells was hybridized with probe A. (c) PCR analysis of tail DNA from Lfc+/+, Lfc+/−, and Lfc−/− mice. Locations of primers used for PCR are indicated with triangles in panel a. (d) Immunoblot analysis of total thymus cell lysates probed for Lfc protein content. (e) Cell morphologies of immature (NT) and mature (+LPS) Lfc wild type (upper-lane) and Lfc-deficient (lower-lane) littermate DCs. Note the presence of multiple veils in both LPS-treated samples. Scale bar, 10 µm. (f) DC differentiation markers (MHC-II and CCR7) of Lfc+/+ (blue line) and Lfc−/− (red line) littermate DCs compared with unstained cells (gray peak). eF450, eFlour 450; PE, Phycoerythrin.