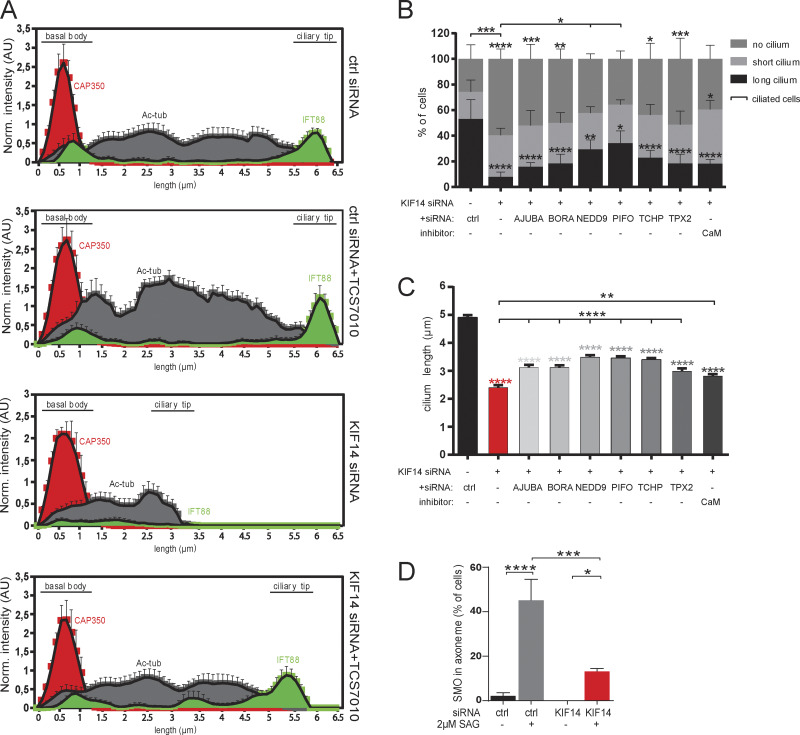
Figure S5.
AURA activity mediates the effects of KIF14 depletion on primary cilia formation. (A) Histograms show localization of CAP350 (red), Ac-tub (gray), and distribution of IFT88 (green) along the primary cilium (N = 5, "norm." means normalized to CAP350) rescued by AURA inhibition (related to to Fig. 7). (B and C) hTERT RPE-1 cells were 48 h transfected with control or KIF14 siRNA, together with either additional siRNA targeting the individual AURA activator or in combination with small-molecule calmidazolium chloride treatment (4 µM) to inhibit calmodulin (CaM) and 24 h serum starved before fixation. (B) Graph showing percentage of ciliated cells and pinpointing NEDD9 and PIFO as modest rescuers of the ciliogenesis defect caused by KIF14 depletion. (C) Graph showing partial cilia length rescues of defects caused by KIF14 depletion by all used AURA activators. (D) Graph quantifying the percentage of cells with SMO localized to the ciliary axoneme after control or KIF14 siRNA transfection, 24 h serum starvation, and 2 µM SAG treatment to HH pathway activation (related to Fig. 8 E). Asterisks indicate statistical significance determined using Tukey's multiple comparisons test.