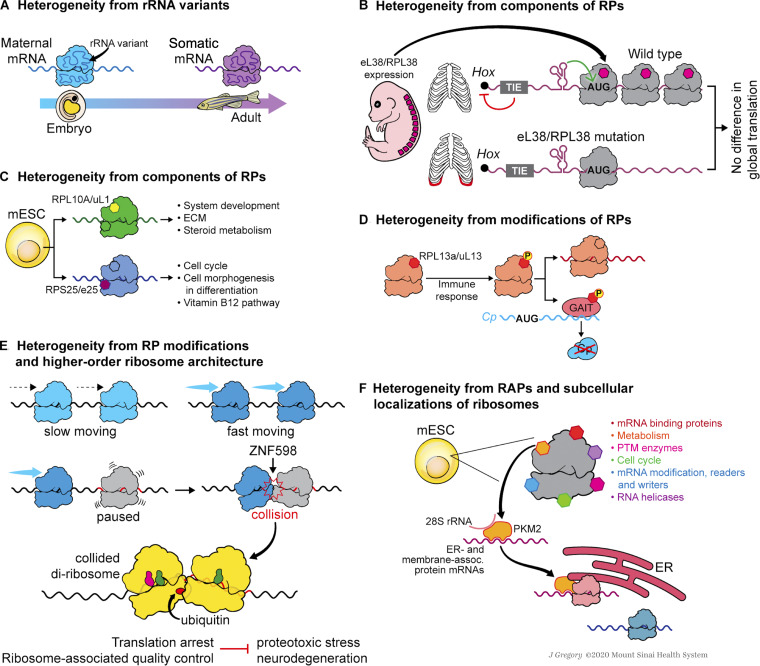
Figure 3.
Ribosome heterogeneity in stem cells and development. (A) During zebrafish embryogenesis, ribosomes switch from a maternal-type rRNA variant to a somatic-type rRNA variant; the former variant has a better affinity for maternal mRNAs, while the latter one prefers maternally nonexpressed mRNAs. (B) RPL38/eL38 is important for the translation of Hox mRNAs, which are necessary for axial skeletal patterning. Within the 5′ UTRs of these Hox mRNAs, a translation inhibitory element (TIE) blocks the canonical cap-dependent translation, and a structured IRES element promotes the recruitment of RPL38/eL38-containing ribosomes. (C) In mESCs, ribosomes containing RPL10A/uL1 or RPS25/eS25 participate in the translation of mRNAs involved in specific cellular pathways. (D) Upon the innate immune response, RPL13A/uL13 is phosphorylated and released from the ribosome. The released phosphorylated RPL13A/uL13 is incorporated into GAIT complex to inhibit the translation of specific inflammation-related ceruloplasmin (Cp) mRNA. (E) The ubiquitin ligase ZNF598 transfers ubiquitin to RPs of the collided diribosomes. Such ubiquitylation is required for translation arrest and the activation of ribosome-associated quality control, the failure of which leads to proteotoxic stress and neurodegeneration. (F) In mESCs, PKM2, as a RAP, is enriched on ER-associated ribosomes and binds mRNAs of ER-associated and membrane-associated proteins to promote their translation. Illustration by Jill K. Gregory.Fig. 3 is reprinted with permission from Mount Sinai Health System.