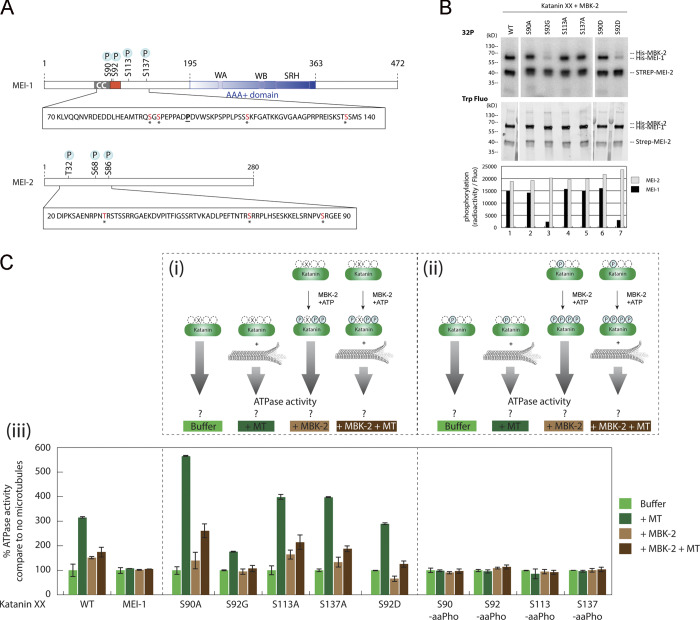
Figure 3.
Phosphorylation of the N-terminal disordered region of MEI-1 inhibits the stimulatory effect of MTs on Katanin ATPase activity. (A) Schematic representation of MEI-1 and MEI-2. The positions of phosphorylated sites identified by LC-MS/MS after in vitro phosphorylation of Katanin by MBK-2 are indicated by asterisks (*). Red box represents the PEST sequence, a predicted interacting site for MEL-26 (Fig. S5). AAA+ domain in blue contains Walker A (WA) and Walker B (WB) motifs as well as second region of homology (SRH). CC, coiled-coil. The position of the gain-of-function mutation P99L is indicated (underlined). (B) Radioactive in vitro kinase assays using MBK-2 kinase and Katanin, WT or containing serine to alanine substitutions in MEI-1 N-terminal at specific positions, as substrates. Autoradiograph of SDS-PAGE showing γ-[32P] incorporation in MEI-1 and MEI-2 (upper panel). Total Katanin present in each lane of the same SDS-PAGE using Stain Free (Bio-Rad), based on tryptophan labeling (middle panel). Graphs showing quantification of the ratio of radioactive MEI-1 and MEI-2 versus the total amount of protein (bottom panel). Gels were quantified using ImageJ, and results are represented in the histogram. The results shown are representative of one experiment that was reproduced three times. (C) Unmodified and phosphorylated Katanin ATPase activity in the absence or presence of MTs. The top panels (Ci and Cii) show the schematics of the experiment and the different Katanin versions used in the assay. Ciii, the bottom panel, shows Katanin ATPase activity presented as percentage of Katanin ATPase activity measured without MTs and without MBK-2. For each Katanin, the measured ATP activity in the absence of MT and MBK-2 was normalized to 100% (first condition, light green bars). (Ci) Katanin (green oval), WT or containing site-specific serine to alanine substitution in MEI-1, was phosphorylated or not by MBK-2, and then the ATPase activity of the enzyme was measured in the absence or presence of MTs. (Cii) Katanin containing MEI-1 phosphorylated at specific sites by genetic code expansion in E. coli was phosphorylated or not by MBK-2, and then the ATPase activity of the enzyme was measured in the absence or presence of MTs. Experiments in each condition were performed at least four times.