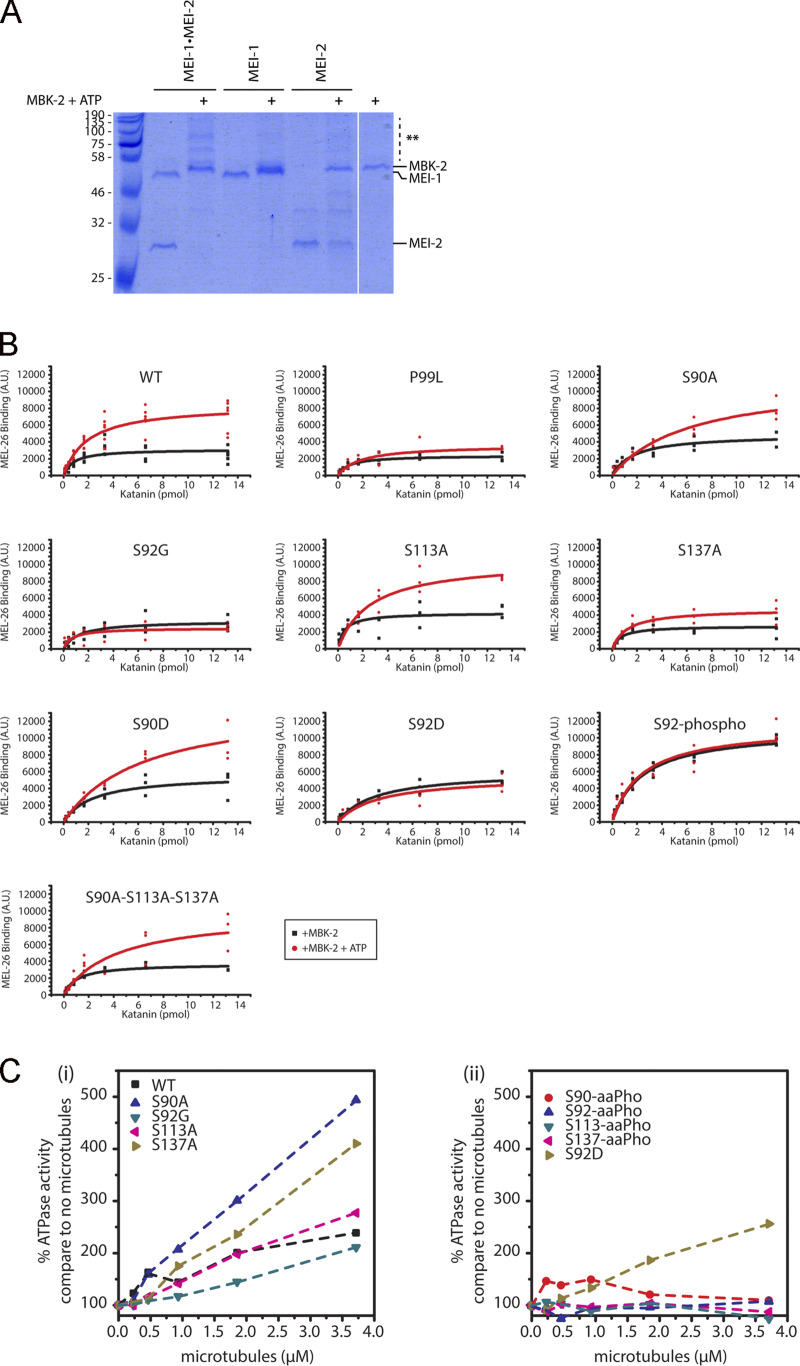
Figure S2.
Phosphorylation of Katanin affects MEL-26 binding and its MT-dependent activity. (A) Qualitative analysis of phosphorylated Katanin on PhosTag SDS-PAGE. Katanin, MEI-1, or MEI-2 phosphorylated or not by MBK-2 ± ATP was separated on PhosTag SDS PAGE 7% to resolve the phosphorylated forms and revealed by Coomassie blue staining. (B) Quantitative analysis of MEL-26 binding to Katanin. Detailed quantification of the MEL-26 interaction detected on DotBlot membranes (presented in Fig. 4). Quantification was performed using ImageJ plugins. Raw values from at least three different experiments were plotted and analyzed using Origin. (C) Phosphorylation of the N-terminal Katanin region inhibits MT-dependent stimulation of Katanin ATPase activity. (Ci) Graphs showing the ATPase activity of Katanin WT and variants in the presence of increasing concentrations of MTs. (Cii) Graphs showing the ATPase activity of Katanin uniquely phosphorylated at specific sites (S-aaPho) compared with a Katanin variant harboring a phosphomimetic residue (S92D) in the presence of increasing concentrations of MTs.