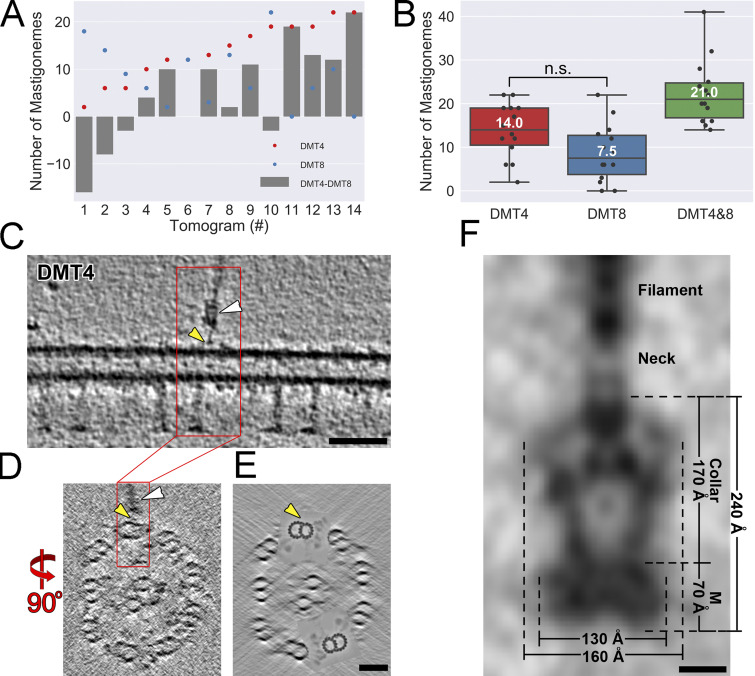
Figure S5.
Mastigonemes are linked to the outer A-B-tubule junction. (A) The numbers of mastigonemes associated with DMTs 4 and 8, respectively (red and blue dots), and their difference (gray bars) in each of 14 tomograms of intact wild-type Chlamydomonas cilia. (B) The distribution of mastigoneme numbers associated with DMT4, DMT8, and their sum in tomograms from intact wild-type Chlamydomonas cilia. n.s., not significant; n = 14 cilia; two-tailed t test. (C–E) Tomographic slices of a representative demembranated wild-type Chlamydomonas cilium, as viewed in longitudinal section (C, which is an enlarged version of an image shown in Fig. 5 E; thickness: 5 nm) and cross sections (D, thickness: 0.5 nm; and E, thickness: 50 nm). A mastigoneme with its base (white arrowheads) is clearly visible, and the anchor site of the thin linker that connects the mastigoneme base to DMT4 is highlighted by yellow arrowheads. For clarity of the DMT structure, DMTs 4 and 8 are highlighted in E by cloning the subtomogram average of the 96-nm DMT repeat back into the raw tomogram for all axonemal repeats along DMT4 and 8. Bars = 50 nm. (F) Dimensions and named regions of the averaged mastigoneme base (also shown in Fig. 5 E) complex in demembranated cilia. The transmembrane disk (M), collar, neck, and mastigoneme filament are marked. Bar = 5 nm.