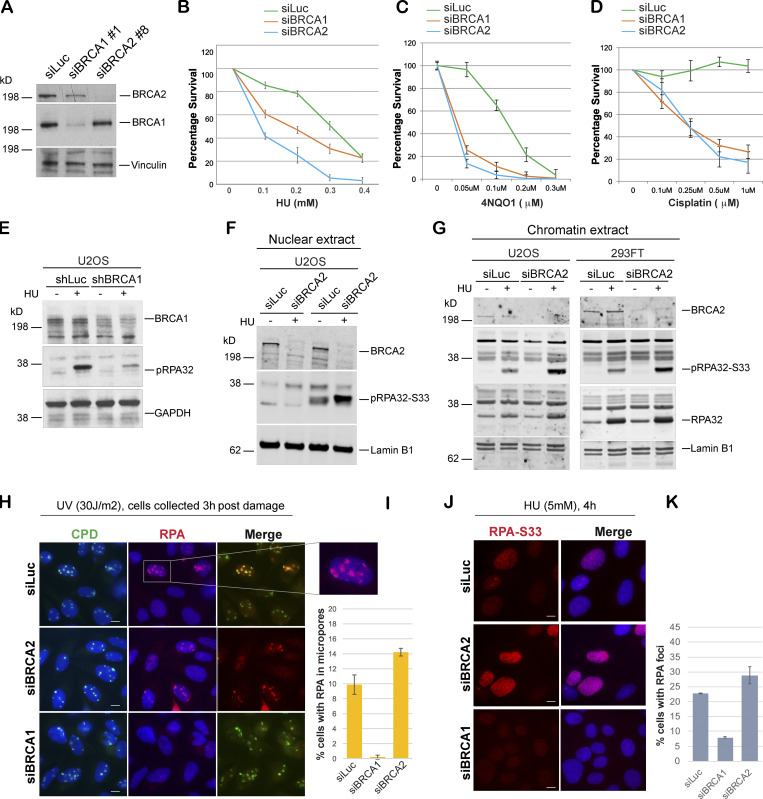
Figure 1.
BRCA1- and BRCA2-depleted cells form different stalled fork intermediates. (A) Western blot analysis of total BRCA1 and BRCA2 protein levels in U2OS cells transfected with siLuc (control), siBRCA1, and siBRCA2. (B–D) CellTiter-Glo–based cell survival assay was used to determine the sensitivity of BRCA1- or BRCA2-deficient cells to various DNA damage–inducing agents. U2OS cells transfected with indicated siRNAs were treated with HU (4 d), 4NQO1 (5 h), or cisplatin (1 d) with indicated doses. Cells were harvested 6 d after the start of the drug treatment, and cell viabilities were tested by detecting the generation of luminescent signal, which is directly proportional to the number of cells present in the culture. Error bars represent SD between triplicates. (E–G) Western blot analysis of RPA32 and pRPA32 (S33) accumulation in control cells and BRCA1- or BRCA2-depleted cells. Cells were treated with 5 mM HU and harvested 3 h after treatment. Whole cell (E), nuclear (F), and chromatin (G) extracts were prepared. (H and I) IF and graph of RPA32 recruitment in U2OS control (siLuc) cells and BRCA1- or BRCA2-depleted cells. Cells were irradiated with 30 J/m2 of UV through a micropore membrane to generate localized sites of DNA damage and harvested 3 h after damage. Cells were costained with RPA32 and CPD. CPD served as marker of the sites of UV damage. Scale bars indicate 10 µm. (J and K) IF and graph of pRPA32-S33 recruitment in U2OS control cells and BRCA1- or BRCA2-depleted cells. Cells were treated with 5 mM HU and harvested 4 h after damage. Cells were stained with pRPA32-S33. Scale bars in J indicate 10 µM. Error bars indicate SD between triplicates.