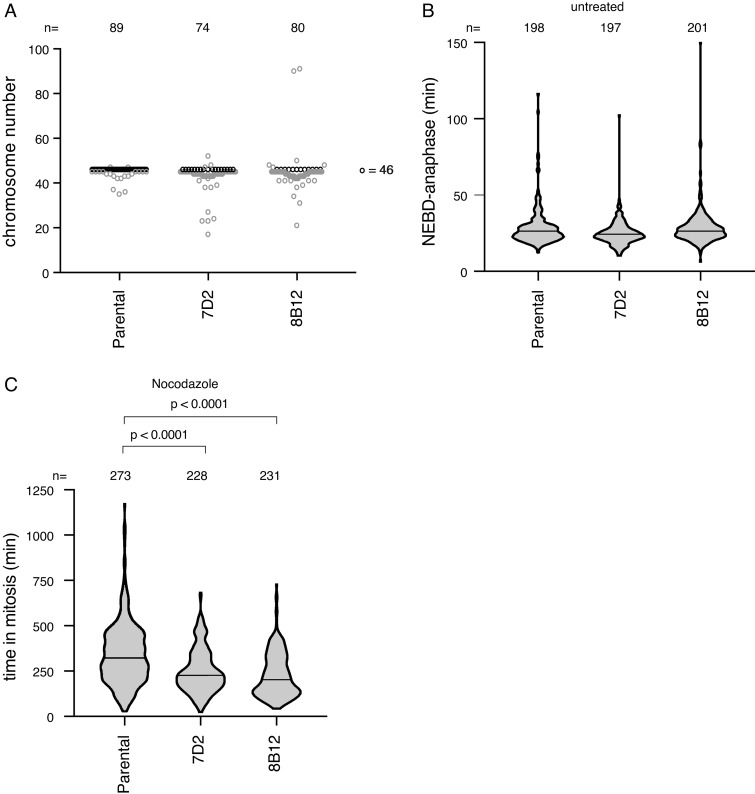
Figure 3.
MAD1 binding to Cyclin B1 is required for genomic stability. (A) Chromosome number per cell was assayed for parental RPE yclin B1-Venus+/−:Ruby-MAD2+/− cells and the MAD1 E53/E56K clones 7D2 and 8B12 by metaphase spreads in three independent experiments. Black dots indicate 46 chromosomes and n indicates the number of cells assayed. Parental n = 89 cells, clone 7D2 n = 74 cells, clone 8B12 n = 80 cells. (B) The time from NEBD to anaphase was measured for parental RPE cyclin B1-Venus+/−:Ruby-MAD2+/− cells and the MAD1 E53/E56K clones 7D2 and 8B12 by time-lapse DIC microscopy. Violin plots show the data from three experiments (median time indicated by the black bar); n indicates the total number of cells analyzed. Parental n = 198 cells, clone 7D2 n = 197 cells, clone 8B12 n = 201 cells. (C) The duration of the mitotic arrest for parental RPE cyclin B1-Venus+/−:Ruby-MAD2+/− cells and the MAD1 E53/E56K clones 7D2 and 8B12 was assayed by time-lapse DIC microscopy in 55 nM nocodazole. Data are plotted as for B; n indicates the total number of cells analyzed. Parental n = 273 cells, clone 7D2 n = 228 cells, clone 8B12 n = 231 cells. The two-tailed P values were calculated using a Mann–Whitney unpaired t test.