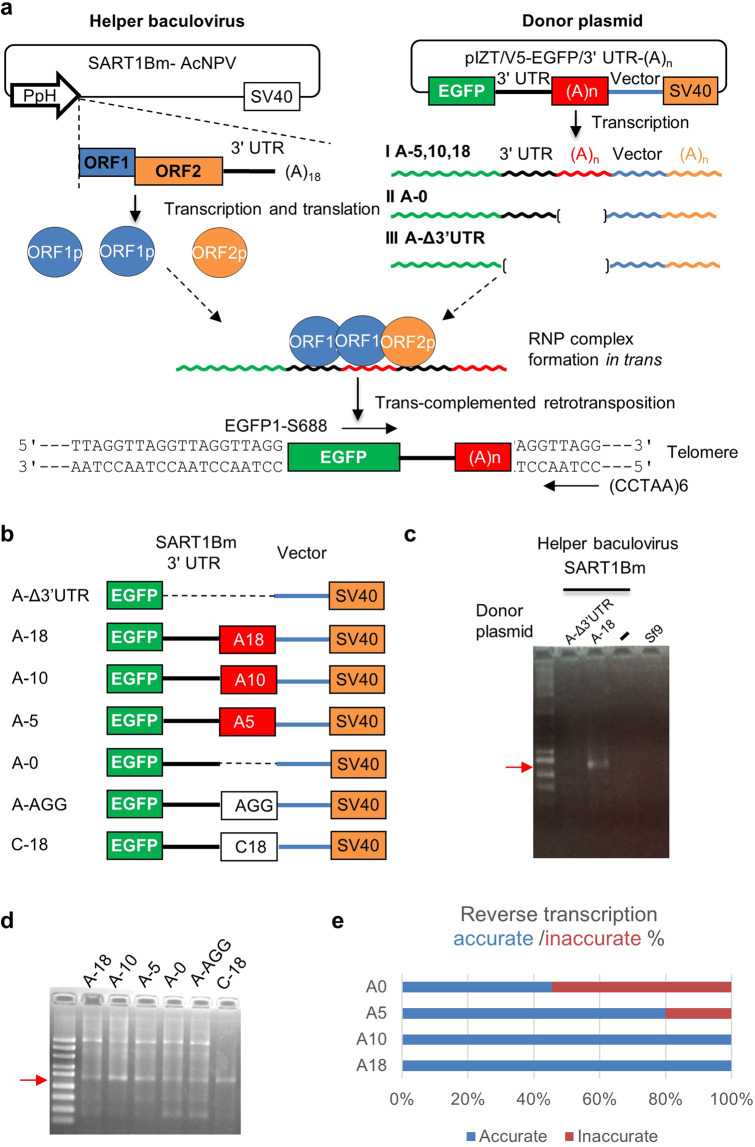
Figure 4.
Trans-in vivo retrotransposition assay in SART1Bm. (a) “Helper” SART1Bm baculovirus (SART1Bm-AcNPV) expresses SART1Bm ORF1p (blue oval) and ORF2p (orange oval). “Donor” plasmids [pIZT/V5-EGFP/3’ UTR-(A)n plasmid] express mRNA of EGFP fused with the SART1Bm 3′ UTR end with variable lengths of poly(A). “Donor” plasmids contain the SV40 polyadenylation signal (SV40). After transfection of “donor” plasmids, the trans-complementation assay measures the ability of “helper” baculovirus to retrotranspose a “donor” EGFP/3’ UTR-(A)n RNA that contains a variable length of poly(A), which leads to the retrotransposition event. Type I has 3’ UTR with two types of poly(A) tail. Type II lacks an encoded poly(A) tail and type III lacks both 3’ UTR and the encoded poly(A) tail. Parentheses indicate the deleted region. The 3′ junction of retrotransposed copies was detected by PCR with primers EGFP1 S688 and (CCTAA)6 (black arrows). RNP indicates the ribonucleoprotein complex. (b) Construct A-Δ3’UTR lacks SART1Bm 3′ UTR and the poly(A) tail. Constructs A-18, A-10, and A-5 contain various lengths of poly(A) tail directly connected to the 3′ UTR end. Construct A-0 lacks a poly(A) tail. Constructs AGG and C-18 contain AGG sequences and poly(C)18 tail directly connected to the 3′ UTR end in place of poly (A) tail, respectively. Dotted line indicates the deleted region. (c) PCR results for the trans-in vivo retrotransposition assay. A-Δ3’UTR, EGFP transfected Sf9 cells with the SART1Bm infection; A-18, EGFP/3’ UTR-(A)18 transfected Sf9 cells with the SART1Bm infection; (−), Sf9 cells with the SART1Bm infection; Sf9, Sf9 cells without the SART1Bm infection. Red arrow indicates the successful trans-in vivo retrotransposition band with the expected size. Molecular sizes are shown on the left. (d) PCR results of trans-in vivo retrotransposition assay. Red arrow indicates the expected PCR band (614 bp + telomeric repeats). (e) Summary of the accurate/inaccurate reverse transcription rates in SART1Bm. When the poly(A) length increased, the rate of inaccurate reverse transcription decreased in both elements.