Fig. 5. Bayesian-DDM with bias and stimulus learning explains identification and categorization task simultaneously.
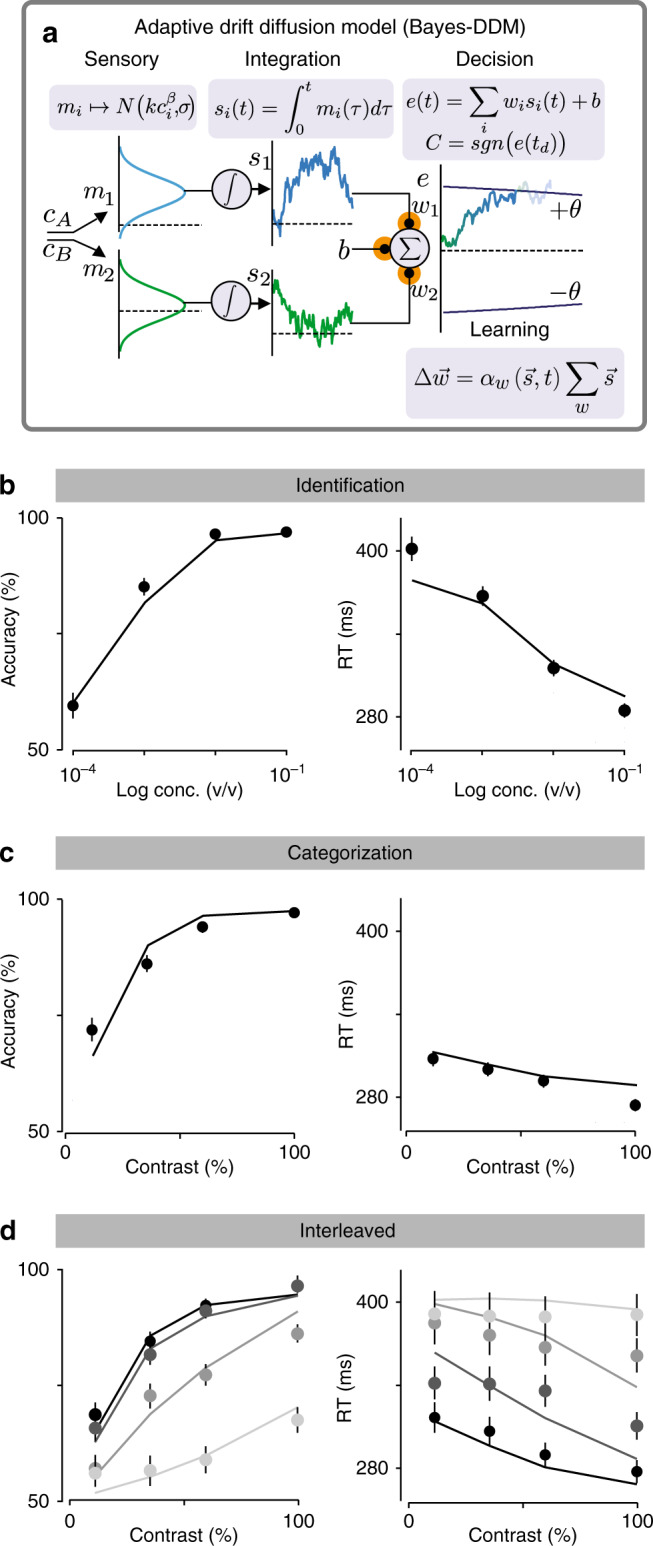
a DDM is even further expanded with the addition of changing stimulus weights, w1 and w2, and trial-by-trial reward-dependent bias b. These weights are then combined with the integrated momentary evidences (s1,s2) plus the offset set by the bias b. After each trial the model updates stimulus weights according to the obtained outcome through a Bayesian learning rule. This model has 10 parameters (Methods). b, c Choice accuracy (fraction of correct trials) and odor sampling duration in identification task (b) and categorization task (c). Solid black line represents model fitted to both tasks (see Methods for more details). d Choice accuracy and odor sampling duration for Interleaved condition. Solid lines represent the obtained fits for Bayes-DDM to this particular data, going from lowest total concentration (lightest gray) to highest (black). Error bars are mean ± SEM over trials and rats.
