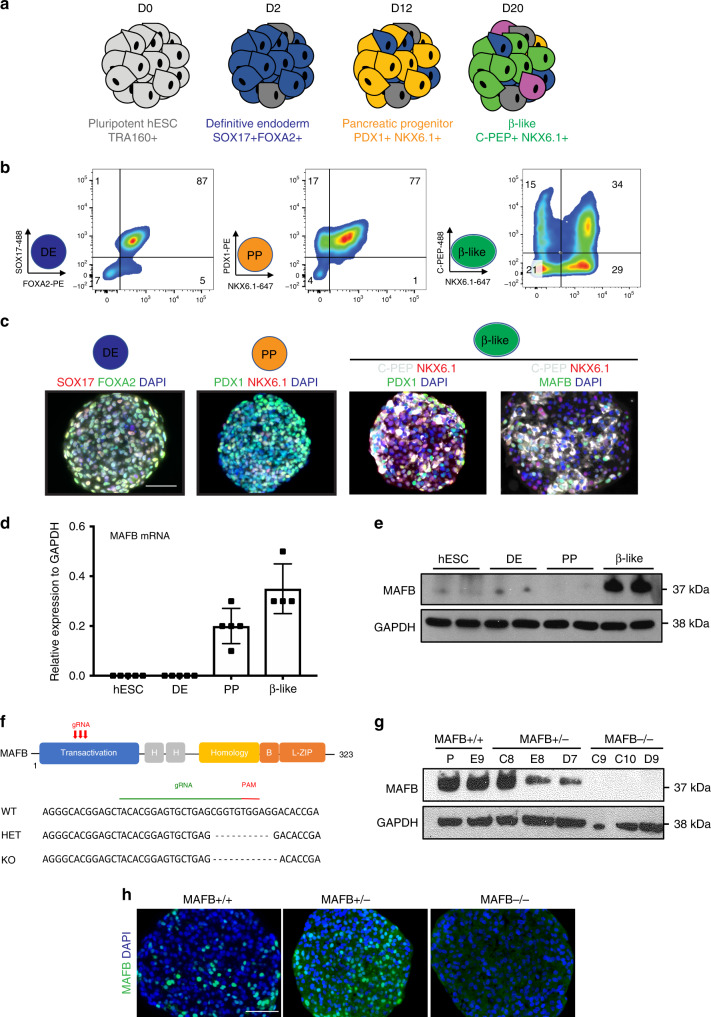
Fig. 1. MAFB is expressed in human β-cell counterparts and generation of MAFB KO hESCs.
a Schematic outlining the differentiation protocol to generate β-like cells from hESCs. The key lineage markers are outlined at each stage. Chemicals and durations for each differentiation stage are indicated in the Methods section. d, day(s); hESC, undifferentiated hESC stage; DE, definitive endoderm stage SOX17 + FOXA2+; PP, pancreatic progenitor stage PDX1 + NKX6.1+; β, β-like cell stage. b Representative FC plots outlining a typical differentiation of cells through the DE, PP, and β-like cell stages using the indicated markers. c Representative IF images from four independent experiments at indicated stages of differentiation depicting SOX17 and FOXA2, PDX1 and NKX6.1, C-PEP co-staining with PDX1 and NKX6.1, and MAFB co-staining with C-PEP and NKX6.1. DAPI indicates nuclear staining. Scale bars, 50 μm. d MAFB mRNA expression during β-cell differentiation as shown via qPCR. Each data point represents an independent biological sample. e Representative western blot from three independent experiments showing MAFB protein levels during β-cell differentiation at the indicated stages. f Targeted disruption of MAFB in hESCs. Targeting strategy for CRISPR-mediated gene editing of MAFB. g Representative western blot analysis of MAFB in targeted clones at the β-cell of differentiation from three independent experiments. Sizes of molecular weight markers are shown on the right. Similar results were obtained using two independent antibodies. h Representative IF images from three independent experiments at the β-cell stage of differentiation depicting MAFB expression in MAFB +/+, +/−, and −/− cells. DAPI indicates nuclear staining. Scale bars, 50 μm.