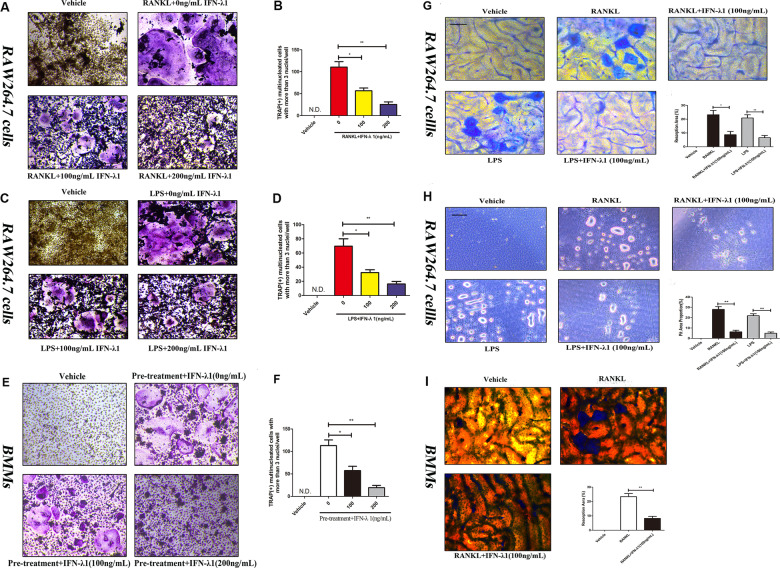
Fig. 4. IFN-λ1 could inhibit osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity, respectively.
a, c, e Representative TRAP stain images of RAW264.7 cells and BMMs treated with RANKL or LPS-induced osteoclastogenesis. b, d, f Quantification of osteoclasts number per well. g RAW264.7 cells were plated on the bone slices and were cultured with RANKL or LPS for 6 days in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml IFN-λ1. Scale bar = 200 μm. Quantification of the bone resorption area on the bone slices. h RAW264.7 cells were plated on the Osteo Assay Surface and were cultured with RANKL or LPS for 6 days in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml IFN-λ1. Scale bar = 200 μm. Quantification of the bone resorption area on the bone slices. i BMMs were plated on the bone slices and were cultured with RANKL for 6 days in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml IFN-λ1. Scale bar = 200 μm. Quantification of the bone resorption area on the bone slices. The data in the figures represent the averages ± SD. N.S. represented as no significant difference. Significant differences are indicated as *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 paired using Student’s t-test unless otherwise specified.